371525
A container of volume 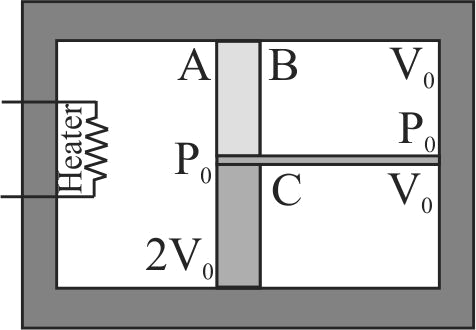
371526
371525
A container of volume 
371526
371525
A container of volume 
371526
371525
A container of volume 
371526
371525
A container of volume 
371526