371525
A container of volume \(4{\rm{ }}{V_0}\) made of a perfectly non-conducting material is divided into two equal parts by a fixed rigid wall whose lower half is non-conducting and upper half is purely conducting. The right side of the wall is divided into equal parts (initially) by means of a massless non-conducting piston free to move as shown. Section \(A\) contains \(2\;mol\) of a gas while the section \(B\) and \(C\) contain \(1\,mol\) each of the same gas \((\gamma=1.5)\) at pressure \(P_{0}\). The heater in left part is switched on till the final pressure in section \(C\) becomes \(125 / 27 P_{0}\). Calculate: Final temperature in part \(A\) :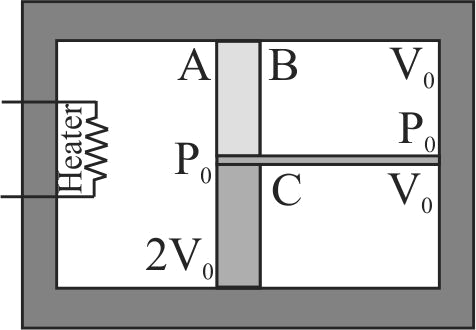
371526 \(7\) moles of a monoatomic ideal gas is enclosed in an adiabatic, vertical cylinder fitted with a smooth, light adiabatic piston. The piston is connected to a vertical spring of spring constant \(420\;N{\rm{/}}m.\) The area of cross-section of the cylinder is \(35\;c{m^2}.\) Initially, the spring is at its natural length and the temperature of the gas is \(30^\circ C.\) The atmospheric pressure is \({10^5}\;Pa.\) The gas is heated slowly for some time by means of an electric heater so as to move the piston up through \(20\;cm.\) Find the work done by the gas
371525
A container of volume \(4{\rm{ }}{V_0}\) made of a perfectly non-conducting material is divided into two equal parts by a fixed rigid wall whose lower half is non-conducting and upper half is purely conducting. The right side of the wall is divided into equal parts (initially) by means of a massless non-conducting piston free to move as shown. Section \(A\) contains \(2\;mol\) of a gas while the section \(B\) and \(C\) contain \(1\,mol\) each of the same gas \((\gamma=1.5)\) at pressure \(P_{0}\). The heater in left part is switched on till the final pressure in section \(C\) becomes \(125 / 27 P_{0}\). Calculate: Final temperature in part \(A\) :
371526 \(7\) moles of a monoatomic ideal gas is enclosed in an adiabatic, vertical cylinder fitted with a smooth, light adiabatic piston. The piston is connected to a vertical spring of spring constant \(420\;N{\rm{/}}m.\) The area of cross-section of the cylinder is \(35\;c{m^2}.\) Initially, the spring is at its natural length and the temperature of the gas is \(30^\circ C.\) The atmospheric pressure is \({10^5}\;Pa.\) The gas is heated slowly for some time by means of an electric heater so as to move the piston up through \(20\;cm.\) Find the work done by the gas
371525
A container of volume \(4{\rm{ }}{V_0}\) made of a perfectly non-conducting material is divided into two equal parts by a fixed rigid wall whose lower half is non-conducting and upper half is purely conducting. The right side of the wall is divided into equal parts (initially) by means of a massless non-conducting piston free to move as shown. Section \(A\) contains \(2\;mol\) of a gas while the section \(B\) and \(C\) contain \(1\,mol\) each of the same gas \((\gamma=1.5)\) at pressure \(P_{0}\). The heater in left part is switched on till the final pressure in section \(C\) becomes \(125 / 27 P_{0}\). Calculate: Final temperature in part \(A\) :
371526 \(7\) moles of a monoatomic ideal gas is enclosed in an adiabatic, vertical cylinder fitted with a smooth, light adiabatic piston. The piston is connected to a vertical spring of spring constant \(420\;N{\rm{/}}m.\) The area of cross-section of the cylinder is \(35\;c{m^2}.\) Initially, the spring is at its natural length and the temperature of the gas is \(30^\circ C.\) The atmospheric pressure is \({10^5}\;Pa.\) The gas is heated slowly for some time by means of an electric heater so as to move the piston up through \(20\;cm.\) Find the work done by the gas
371525
A container of volume \(4{\rm{ }}{V_0}\) made of a perfectly non-conducting material is divided into two equal parts by a fixed rigid wall whose lower half is non-conducting and upper half is purely conducting. The right side of the wall is divided into equal parts (initially) by means of a massless non-conducting piston free to move as shown. Section \(A\) contains \(2\;mol\) of a gas while the section \(B\) and \(C\) contain \(1\,mol\) each of the same gas \((\gamma=1.5)\) at pressure \(P_{0}\). The heater in left part is switched on till the final pressure in section \(C\) becomes \(125 / 27 P_{0}\). Calculate: Final temperature in part \(A\) :
371526 \(7\) moles of a monoatomic ideal gas is enclosed in an adiabatic, vertical cylinder fitted with a smooth, light adiabatic piston. The piston is connected to a vertical spring of spring constant \(420\;N{\rm{/}}m.\) The area of cross-section of the cylinder is \(35\;c{m^2}.\) Initially, the spring is at its natural length and the temperature of the gas is \(30^\circ C.\) The atmospheric pressure is \({10^5}\;Pa.\) The gas is heated slowly for some time by means of an electric heater so as to move the piston up through \(20\;cm.\) Find the work done by the gas
371525
A container of volume \(4{\rm{ }}{V_0}\) made of a perfectly non-conducting material is divided into two equal parts by a fixed rigid wall whose lower half is non-conducting and upper half is purely conducting. The right side of the wall is divided into equal parts (initially) by means of a massless non-conducting piston free to move as shown. Section \(A\) contains \(2\;mol\) of a gas while the section \(B\) and \(C\) contain \(1\,mol\) each of the same gas \((\gamma=1.5)\) at pressure \(P_{0}\). The heater in left part is switched on till the final pressure in section \(C\) becomes \(125 / 27 P_{0}\). Calculate: Final temperature in part \(A\) :
371526 \(7\) moles of a monoatomic ideal gas is enclosed in an adiabatic, vertical cylinder fitted with a smooth, light adiabatic piston. The piston is connected to a vertical spring of spring constant \(420\;N{\rm{/}}m.\) The area of cross-section of the cylinder is \(35\;c{m^2}.\) Initially, the spring is at its natural length and the temperature of the gas is \(30^\circ C.\) The atmospheric pressure is \({10^5}\;Pa.\) The gas is heated slowly for some time by means of an electric heater so as to move the piston up through \(20\;cm.\) Find the work done by the gas
