369797
A copper wire of length
369798
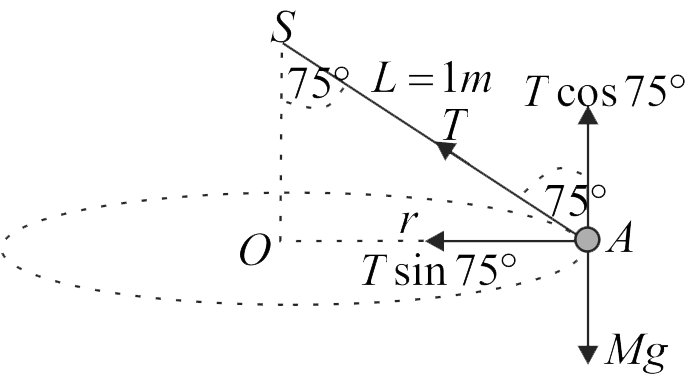
A stone of
369797
A copper wire of length
369798
A stone of
369797
A copper wire of length
369798
A stone of
369797
A copper wire of length
369798
A stone of