369792
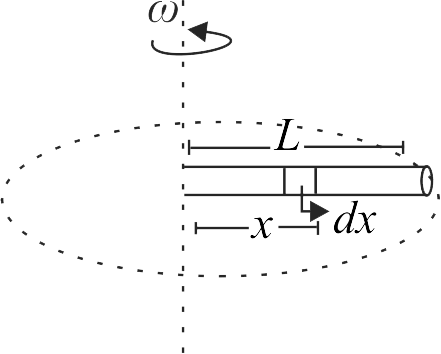
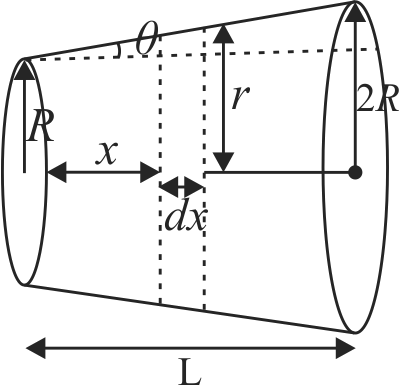
A uniformly tapering conical wire is made from a material of Young's modulus Y and has a normal, unextended length L. The radii, at the upper and lower ends of this conical wire, have values
369792
A uniformly tapering conical wire is made from a material of Young's modulus Y and has a normal, unextended length L. The radii, at the upper and lower ends of this conical wire, have values
369792
A uniformly tapering conical wire is made from a material of Young's modulus Y and has a normal, unextended length L. The radii, at the upper and lower ends of this conical wire, have values
369792
A uniformly tapering conical wire is made from a material of Young's modulus Y and has a normal, unextended length L. The radii, at the upper and lower ends of this conical wire, have values
369792
A uniformly tapering conical wire is made from a material of Young's modulus Y and has a normal, unextended length L. The radii, at the upper and lower ends of this conical wire, have values