360180
Two spherical vessels of equal volume, are connected by a narrow tube. The apparatus contains an ideal gas at one atmosphere and at temperature \(300 K\). Now if one vessel is immersed in a bath of constant temperature \(600 K\) and the other in a bath of constant temperature \(300 K\). Then the common pressure will be
360181
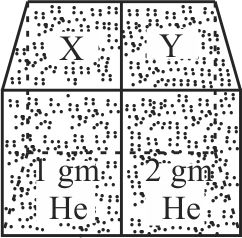
Two identical vessels contain the same gas at pressures \(P_{1}\) and \(P_{2}\) at absoulte temperatures \(T_{1}\) and \(T_{2}\), respectively. On joining the vessels with a small tube as shown in the figure, the gas reaches a common temperature \(T\) and \(a\) common pressure \(P\). Determine the ratio \(P / T\).
360180
Two spherical vessels of equal volume, are connected by a narrow tube. The apparatus contains an ideal gas at one atmosphere and at temperature \(300 K\). Now if one vessel is immersed in a bath of constant temperature \(600 K\) and the other in a bath of constant temperature \(300 K\). Then the common pressure will be
360181
Two identical vessels contain the same gas at pressures \(P_{1}\) and \(P_{2}\) at absoulte temperatures \(T_{1}\) and \(T_{2}\), respectively. On joining the vessels with a small tube as shown in the figure, the gas reaches a common temperature \(T\) and \(a\) common pressure \(P\). Determine the ratio \(P / T\).
360180
Two spherical vessels of equal volume, are connected by a narrow tube. The apparatus contains an ideal gas at one atmosphere and at temperature \(300 K\). Now if one vessel is immersed in a bath of constant temperature \(600 K\) and the other in a bath of constant temperature \(300 K\). Then the common pressure will be
360181
Two identical vessels contain the same gas at pressures \(P_{1}\) and \(P_{2}\) at absoulte temperatures \(T_{1}\) and \(T_{2}\), respectively. On joining the vessels with a small tube as shown in the figure, the gas reaches a common temperature \(T\) and \(a\) common pressure \(P\). Determine the ratio \(P / T\).
360180
Two spherical vessels of equal volume, are connected by a narrow tube. The apparatus contains an ideal gas at one atmosphere and at temperature \(300 K\). Now if one vessel is immersed in a bath of constant temperature \(600 K\) and the other in a bath of constant temperature \(300 K\). Then the common pressure will be
360181
Two identical vessels contain the same gas at pressures \(P_{1}\) and \(P_{2}\) at absoulte temperatures \(T_{1}\) and \(T_{2}\), respectively. On joining the vessels with a small tube as shown in the figure, the gas reaches a common temperature \(T\) and \(a\) common pressure \(P\). Determine the ratio \(P / T\).
360180
Two spherical vessels of equal volume, are connected by a narrow tube. The apparatus contains an ideal gas at one atmosphere and at temperature \(300 K\). Now if one vessel is immersed in a bath of constant temperature \(600 K\) and the other in a bath of constant temperature \(300 K\). Then the common pressure will be
360181
Two identical vessels contain the same gas at pressures \(P_{1}\) and \(P_{2}\) at absoulte temperatures \(T_{1}\) and \(T_{2}\), respectively. On joining the vessels with a small tube as shown in the figure, the gas reaches a common temperature \(T\) and \(a\) common pressure \(P\). Determine the ratio \(P / T\).