354716
A source of sound emits sound waves at frequency 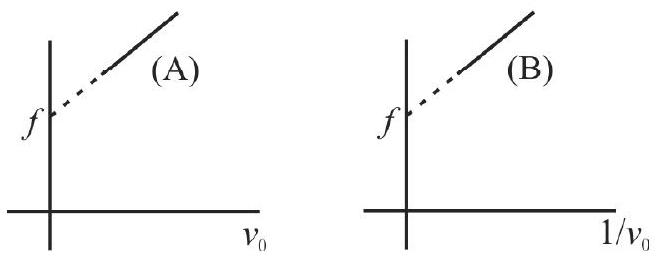
354716
A source of sound emits sound waves at frequency 
354716
A source of sound emits sound waves at frequency 
354716
A source of sound emits sound waves at frequency 