365363
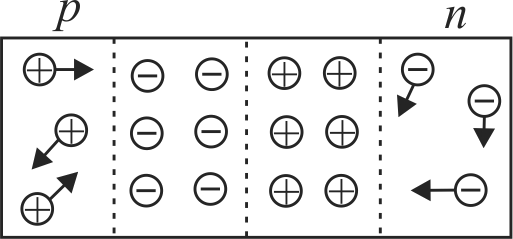
The current through any \(p-n\) junction is due to
A. Drift of charge carriers
B. Diffusion of charge carriers
C. Different concentrations of same type of charge carriers in different regions
D. Same concentrations of same type of charge carriers in different regions
365363
The current through any \(p-n\) junction is due to
A. Drift of charge carriers
B. Diffusion of charge carriers
C. Different concentrations of same type of charge carriers in different regions
D. Same concentrations of same type of charge carriers in different regions
365363
The current through any \(p-n\) junction is due to
A. Drift of charge carriers
B. Diffusion of charge carriers
C. Different concentrations of same type of charge carriers in different regions
D. Same concentrations of same type of charge carriers in different regions
365363
The current through any \(p-n\) junction is due to
A. Drift of charge carriers
B. Diffusion of charge carriers
C. Different concentrations of same type of charge carriers in different regions
D. Same concentrations of same type of charge carriers in different regions