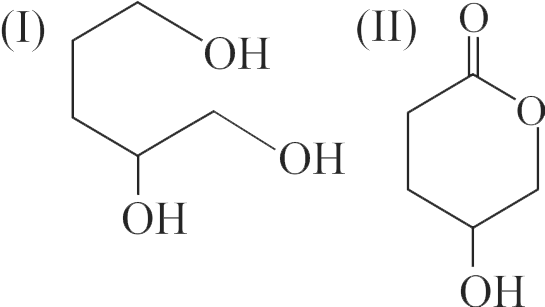
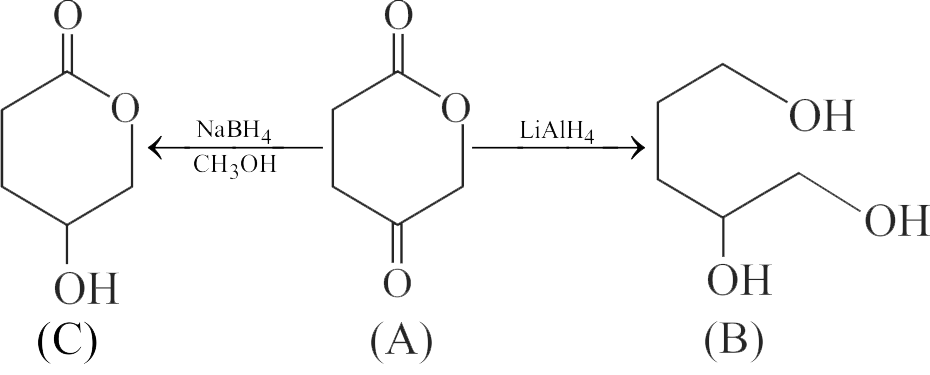
322880
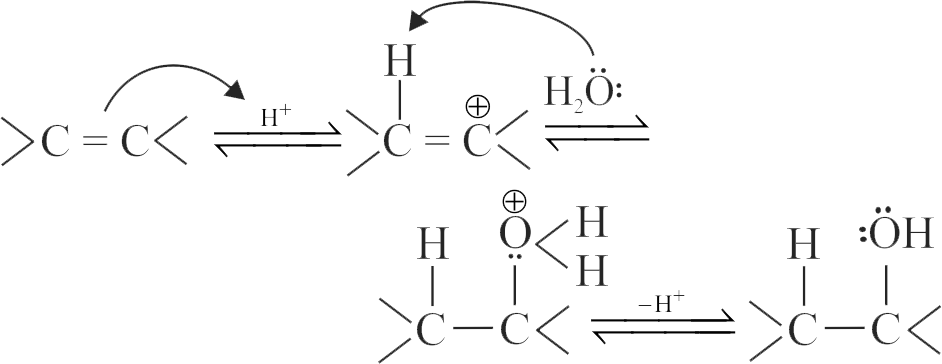
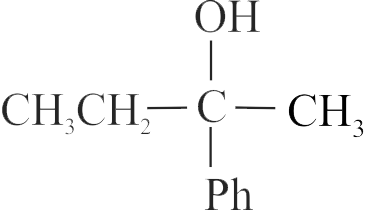
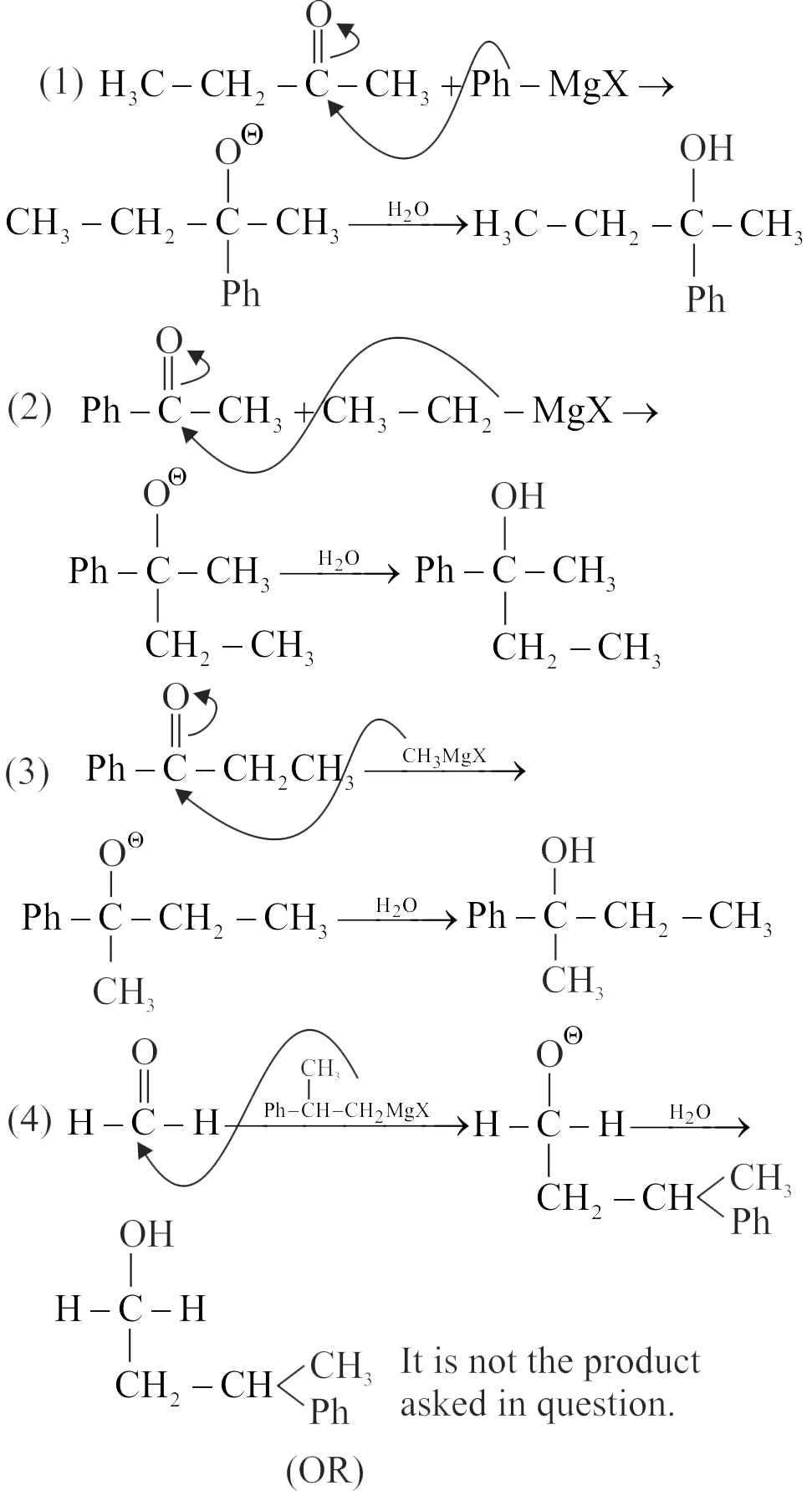
The acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes involves the following three steps:
I. Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
II. Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of \(\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{O}^{+}\).
III. Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
Identify the sequence for the mechanism of reaction in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.
322880
The acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes involves the following three steps:
I. Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
II. Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of \(\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{O}^{+}\).
III. Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
Identify the sequence for the mechanism of reaction in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.
322880
The acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes involves the following three steps:
I. Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
II. Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of \(\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{O}^{+}\).
III. Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
Identify the sequence for the mechanism of reaction in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.
322880
The acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes involves the following three steps:
I. Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
II. Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of \(\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{O}^{+}\).
III. Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
Identify the sequence for the mechanism of reaction in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.
322880
The acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes involves the following three steps:
I. Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
II. Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of \(\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{O}^{+}\).
III. Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
Identify the sequence for the mechanism of reaction in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.