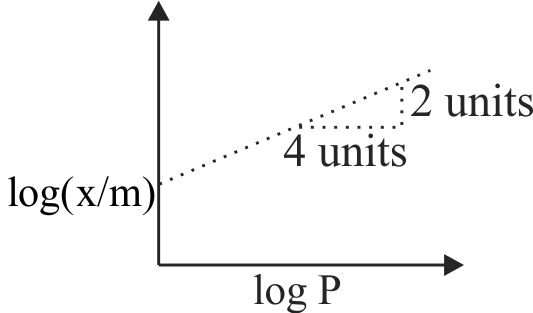
320826
Which of the following relation is correct?
(i) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)=constant at high pressure
(ii) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)= constant X \({{\rm{P}}^{{\rm{1/n}}}}\) at intermediate pressure
(iii) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)= constant X \({\text{ P}}\) at lower pressure
320828 Calculate the surface area of a catalyst that adsorbs \(10^{3} \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\) of \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}\) (reduced to STP) per gram in order to form the monolayer. The effective area occupied by \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}\) molecule of the surface is \(1.62 \times 10^{-15} \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)
320826
Which of the following relation is correct?
(i) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)=constant at high pressure
(ii) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)= constant X \({{\rm{P}}^{{\rm{1/n}}}}\) at intermediate pressure
(iii) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)= constant X \({\text{ P}}\) at lower pressure
320828 Calculate the surface area of a catalyst that adsorbs \(10^{3} \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\) of \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}\) (reduced to STP) per gram in order to form the monolayer. The effective area occupied by \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}\) molecule of the surface is \(1.62 \times 10^{-15} \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)
320826
Which of the following relation is correct?
(i) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)=constant at high pressure
(ii) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)= constant X \({{\rm{P}}^{{\rm{1/n}}}}\) at intermediate pressure
(iii) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)= constant X \({\text{ P}}\) at lower pressure
320828 Calculate the surface area of a catalyst that adsorbs \(10^{3} \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\) of \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}\) (reduced to STP) per gram in order to form the monolayer. The effective area occupied by \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}\) molecule of the surface is \(1.62 \times 10^{-15} \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)
320826
Which of the following relation is correct?
(i) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)=constant at high pressure
(ii) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)= constant X \({{\rm{P}}^{{\rm{1/n}}}}\) at intermediate pressure
(iii) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)= constant X \({\text{ P}}\) at lower pressure
320828 Calculate the surface area of a catalyst that adsorbs \(10^{3} \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\) of \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}\) (reduced to STP) per gram in order to form the monolayer. The effective area occupied by \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}\) molecule of the surface is \(1.62 \times 10^{-15} \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)
320826
Which of the following relation is correct?
(i) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)=constant at high pressure
(ii) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)= constant X \({{\rm{P}}^{{\rm{1/n}}}}\) at intermediate pressure
(iii) \(\frac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{m}}}\)= constant X \({\text{ P}}\) at lower pressure
320828 Calculate the surface area of a catalyst that adsorbs \(10^{3} \mathrm{~cm}^{3}\) of \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}\) (reduced to STP) per gram in order to form the monolayer. The effective area occupied by \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}\) molecule of the surface is \(1.62 \times 10^{-15} \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\)