282105
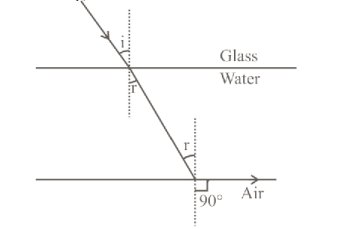
Consider a glass and water interface. If a light ray incident at the glass water interface with an angle of ' $i$ ' and the ray emerges parallel to surface of water. What is refractive index of glass?
1 1
2 1.5
3 $\frac{1}{\sin \mathrm{i}}$
4 $\sin \mathrm{i}$
Explanation:
C: Given, incident angle $=\mathrm{i}$
Refractive index of water $=\mu_{\mathrm{w}}$
And reflection angle at water air interface is $90^{\circ}$
\begin{tabular}{l}
Applying Snell's law at water air interface \\
$\mu_w \sin r=\mu_{\text {air }} \sin 90^{\circ}$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{w}} \sin r=1$ \\
Applying Snell's law at water glass interface \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}} \sin \mathrm{i}=\mu_{\mathrm{w}} \sin \mathrm{r}$ \\
From equation $(\mathrm{i})$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}} \sin \mathrm{i}=1$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}}=\frac{1}{\sin \mathrm{i}}$
\end{tabular}
TS EAMCET 29.09.2020
Ray Optics
282106
A light travels through water in the breaker. The height of water column is ' $h$ '. Refractive index of water is ' $\mu_w$ '. If $c$ is velocity of light in air, the time taken by light to travel through water will be
D: We know that,
$\text { Velocity }=\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { time }}$
or time $=\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { velocity }}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{c} / \mu_{\mathrm{w}}}$
$\left(\begin{array}{rl}
\because \mu_{\mathrm{w}} & =\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\mathrm{v} & =\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mu_{\mathrm{w}}}
\end{array}\right)$
Where, $\mathrm{c}=$ speed of light in air
$\mu_{\mathrm{w}}=\text { Refractive index of water }$
So, $\quad$ time $=\frac{h \mu_w}{c}$
MHT-CET 2020
Ray Optics
282107
Refractive index of the medium is ' $\mu$ ' and wavelength is $\lambda$, then which of the following proportionality relation is correct?
1 $\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda}$
2 $\mu \propto \lambda$
3 $\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda^2}$
4 $\mu \propto \lambda^2$
Explanation:
A: Given, Reflective index $=\mu$, wavelength $=\lambda$
We know that,
$\begin{aligned}
\mu=\frac{\text { speed of light in air }}{\text { speed of light in medium }} \\
\mu=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\lambda \mathrm{f}} \quad(\because \mathrm{v}=\lambda \mathrm{f}) \\
\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda}
\end{aligned}$
MHT-CET 2020
Ray Optics
282108
Let ' $\mu_1$ ' and ' $\mu_2$ ' be the refractive indices of two media. ' $v_1$ ' and ' $v_2$ ' are the velocities of light in the media respectively. Which one of the following relations is TRUE?
1 $\mu_2^2 v_1=\mu_1^2 v_2$
2 $\mu_1 \mathrm{v}_1=\mu_2 \mathrm{v}_2$
3 $\mu_2 v_1=\mu_1 v_2$
4 $\mu_1 v_1^2=\mu_2 v_2^2$
Explanation:
B: Given, $\mu_1$ and $\mu_2$ be the refractive indices of two media, $v_1$ and $v_2$ are the velocities.
We know that,
${ }_1 \mu_2=\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}=\frac{\text { speed of light in medium } 1}{\text { speed of light in medium } 2}=\frac{v_1}{v_2}$
$\mu_1 \mathrm{v}_1=\mu_2 \mathrm{v}_2$
282105
Consider a glass and water interface. If a light ray incident at the glass water interface with an angle of ' $i$ ' and the ray emerges parallel to surface of water. What is refractive index of glass?
1 1
2 1.5
3 $\frac{1}{\sin \mathrm{i}}$
4 $\sin \mathrm{i}$
Explanation:
C: Given, incident angle $=\mathrm{i}$
Refractive index of water $=\mu_{\mathrm{w}}$
And reflection angle at water air interface is $90^{\circ}$

\begin{tabular}{l}
Applying Snell's law at water air interface \\
$\mu_w \sin r=\mu_{\text {air }} \sin 90^{\circ}$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{w}} \sin r=1$ \\
Applying Snell's law at water glass interface \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}} \sin \mathrm{i}=\mu_{\mathrm{w}} \sin \mathrm{r}$ \\
From equation $(\mathrm{i})$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}} \sin \mathrm{i}=1$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}}=\frac{1}{\sin \mathrm{i}}$
\end{tabular}
TS EAMCET 29.09.2020
Ray Optics
282106
A light travels through water in the breaker. The height of water column is ' $h$ '. Refractive index of water is ' $\mu_w$ '. If $c$ is velocity of light in air, the time taken by light to travel through water will be
D: We know that,
$\text { Velocity }=\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { time }}$
or time $=\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { velocity }}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{c} / \mu_{\mathrm{w}}}$
$\left(\begin{array}{rl}
\because \mu_{\mathrm{w}} & =\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\mathrm{v} & =\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mu_{\mathrm{w}}}
\end{array}\right)$
Where, $\mathrm{c}=$ speed of light in air
$\mu_{\mathrm{w}}=\text { Refractive index of water }$
So, $\quad$ time $=\frac{h \mu_w}{c}$
MHT-CET 2020
Ray Optics
282107
Refractive index of the medium is ' $\mu$ ' and wavelength is $\lambda$, then which of the following proportionality relation is correct?
1 $\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda}$
2 $\mu \propto \lambda$
3 $\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda^2}$
4 $\mu \propto \lambda^2$
Explanation:
A: Given, Reflective index $=\mu$, wavelength $=\lambda$
We know that,
$\begin{aligned}
\mu=\frac{\text { speed of light in air }}{\text { speed of light in medium }} \\
\mu=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\lambda \mathrm{f}} \quad(\because \mathrm{v}=\lambda \mathrm{f}) \\
\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda}
\end{aligned}$
MHT-CET 2020
Ray Optics
282108
Let ' $\mu_1$ ' and ' $\mu_2$ ' be the refractive indices of two media. ' $v_1$ ' and ' $v_2$ ' are the velocities of light in the media respectively. Which one of the following relations is TRUE?
1 $\mu_2^2 v_1=\mu_1^2 v_2$
2 $\mu_1 \mathrm{v}_1=\mu_2 \mathrm{v}_2$
3 $\mu_2 v_1=\mu_1 v_2$
4 $\mu_1 v_1^2=\mu_2 v_2^2$
Explanation:
B: Given, $\mu_1$ and $\mu_2$ be the refractive indices of two media, $v_1$ and $v_2$ are the velocities.
We know that,
${ }_1 \mu_2=\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}=\frac{\text { speed of light in medium } 1}{\text { speed of light in medium } 2}=\frac{v_1}{v_2}$
$\mu_1 \mathrm{v}_1=\mu_2 \mathrm{v}_2$
282105
Consider a glass and water interface. If a light ray incident at the glass water interface with an angle of ' $i$ ' and the ray emerges parallel to surface of water. What is refractive index of glass?
1 1
2 1.5
3 $\frac{1}{\sin \mathrm{i}}$
4 $\sin \mathrm{i}$
Explanation:
C: Given, incident angle $=\mathrm{i}$
Refractive index of water $=\mu_{\mathrm{w}}$
And reflection angle at water air interface is $90^{\circ}$

\begin{tabular}{l}
Applying Snell's law at water air interface \\
$\mu_w \sin r=\mu_{\text {air }} \sin 90^{\circ}$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{w}} \sin r=1$ \\
Applying Snell's law at water glass interface \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}} \sin \mathrm{i}=\mu_{\mathrm{w}} \sin \mathrm{r}$ \\
From equation $(\mathrm{i})$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}} \sin \mathrm{i}=1$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}}=\frac{1}{\sin \mathrm{i}}$
\end{tabular}
TS EAMCET 29.09.2020
Ray Optics
282106
A light travels through water in the breaker. The height of water column is ' $h$ '. Refractive index of water is ' $\mu_w$ '. If $c$ is velocity of light in air, the time taken by light to travel through water will be
D: We know that,
$\text { Velocity }=\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { time }}$
or time $=\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { velocity }}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{c} / \mu_{\mathrm{w}}}$
$\left(\begin{array}{rl}
\because \mu_{\mathrm{w}} & =\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\mathrm{v} & =\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mu_{\mathrm{w}}}
\end{array}\right)$
Where, $\mathrm{c}=$ speed of light in air
$\mu_{\mathrm{w}}=\text { Refractive index of water }$
So, $\quad$ time $=\frac{h \mu_w}{c}$
MHT-CET 2020
Ray Optics
282107
Refractive index of the medium is ' $\mu$ ' and wavelength is $\lambda$, then which of the following proportionality relation is correct?
1 $\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda}$
2 $\mu \propto \lambda$
3 $\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda^2}$
4 $\mu \propto \lambda^2$
Explanation:
A: Given, Reflective index $=\mu$, wavelength $=\lambda$
We know that,
$\begin{aligned}
\mu=\frac{\text { speed of light in air }}{\text { speed of light in medium }} \\
\mu=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\lambda \mathrm{f}} \quad(\because \mathrm{v}=\lambda \mathrm{f}) \\
\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda}
\end{aligned}$
MHT-CET 2020
Ray Optics
282108
Let ' $\mu_1$ ' and ' $\mu_2$ ' be the refractive indices of two media. ' $v_1$ ' and ' $v_2$ ' are the velocities of light in the media respectively. Which one of the following relations is TRUE?
1 $\mu_2^2 v_1=\mu_1^2 v_2$
2 $\mu_1 \mathrm{v}_1=\mu_2 \mathrm{v}_2$
3 $\mu_2 v_1=\mu_1 v_2$
4 $\mu_1 v_1^2=\mu_2 v_2^2$
Explanation:
B: Given, $\mu_1$ and $\mu_2$ be the refractive indices of two media, $v_1$ and $v_2$ are the velocities.
We know that,
${ }_1 \mu_2=\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}=\frac{\text { speed of light in medium } 1}{\text { speed of light in medium } 2}=\frac{v_1}{v_2}$
$\mu_1 \mathrm{v}_1=\mu_2 \mathrm{v}_2$
282105
Consider a glass and water interface. If a light ray incident at the glass water interface with an angle of ' $i$ ' and the ray emerges parallel to surface of water. What is refractive index of glass?
1 1
2 1.5
3 $\frac{1}{\sin \mathrm{i}}$
4 $\sin \mathrm{i}$
Explanation:
C: Given, incident angle $=\mathrm{i}$
Refractive index of water $=\mu_{\mathrm{w}}$
And reflection angle at water air interface is $90^{\circ}$

\begin{tabular}{l}
Applying Snell's law at water air interface \\
$\mu_w \sin r=\mu_{\text {air }} \sin 90^{\circ}$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{w}} \sin r=1$ \\
Applying Snell's law at water glass interface \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}} \sin \mathrm{i}=\mu_{\mathrm{w}} \sin \mathrm{r}$ \\
From equation $(\mathrm{i})$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}} \sin \mathrm{i}=1$ \\
$\mu_{\mathrm{g}}=\frac{1}{\sin \mathrm{i}}$
\end{tabular}
TS EAMCET 29.09.2020
Ray Optics
282106
A light travels through water in the breaker. The height of water column is ' $h$ '. Refractive index of water is ' $\mu_w$ '. If $c$ is velocity of light in air, the time taken by light to travel through water will be
D: We know that,
$\text { Velocity }=\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { time }}$
or time $=\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { velocity }}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{c} / \mu_{\mathrm{w}}}$
$\left(\begin{array}{rl}
\because \mu_{\mathrm{w}} & =\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\mathrm{v} & =\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mu_{\mathrm{w}}}
\end{array}\right)$
Where, $\mathrm{c}=$ speed of light in air
$\mu_{\mathrm{w}}=\text { Refractive index of water }$
So, $\quad$ time $=\frac{h \mu_w}{c}$
MHT-CET 2020
Ray Optics
282107
Refractive index of the medium is ' $\mu$ ' and wavelength is $\lambda$, then which of the following proportionality relation is correct?
1 $\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda}$
2 $\mu \propto \lambda$
3 $\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda^2}$
4 $\mu \propto \lambda^2$
Explanation:
A: Given, Reflective index $=\mu$, wavelength $=\lambda$
We know that,
$\begin{aligned}
\mu=\frac{\text { speed of light in air }}{\text { speed of light in medium }} \\
\mu=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\lambda \mathrm{f}} \quad(\because \mathrm{v}=\lambda \mathrm{f}) \\
\mu \propto \frac{1}{\lambda}
\end{aligned}$
MHT-CET 2020
Ray Optics
282108
Let ' $\mu_1$ ' and ' $\mu_2$ ' be the refractive indices of two media. ' $v_1$ ' and ' $v_2$ ' are the velocities of light in the media respectively. Which one of the following relations is TRUE?
1 $\mu_2^2 v_1=\mu_1^2 v_2$
2 $\mu_1 \mathrm{v}_1=\mu_2 \mathrm{v}_2$
3 $\mu_2 v_1=\mu_1 v_2$
4 $\mu_1 v_1^2=\mu_2 v_2^2$
Explanation:
B: Given, $\mu_1$ and $\mu_2$ be the refractive indices of two media, $v_1$ and $v_2$ are the velocities.
We know that,
${ }_1 \mu_2=\frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}=\frac{\text { speed of light in medium } 1}{\text { speed of light in medium } 2}=\frac{v_1}{v_2}$
$\mu_1 \mathrm{v}_1=\mu_2 \mathrm{v}_2$