142147
The graph 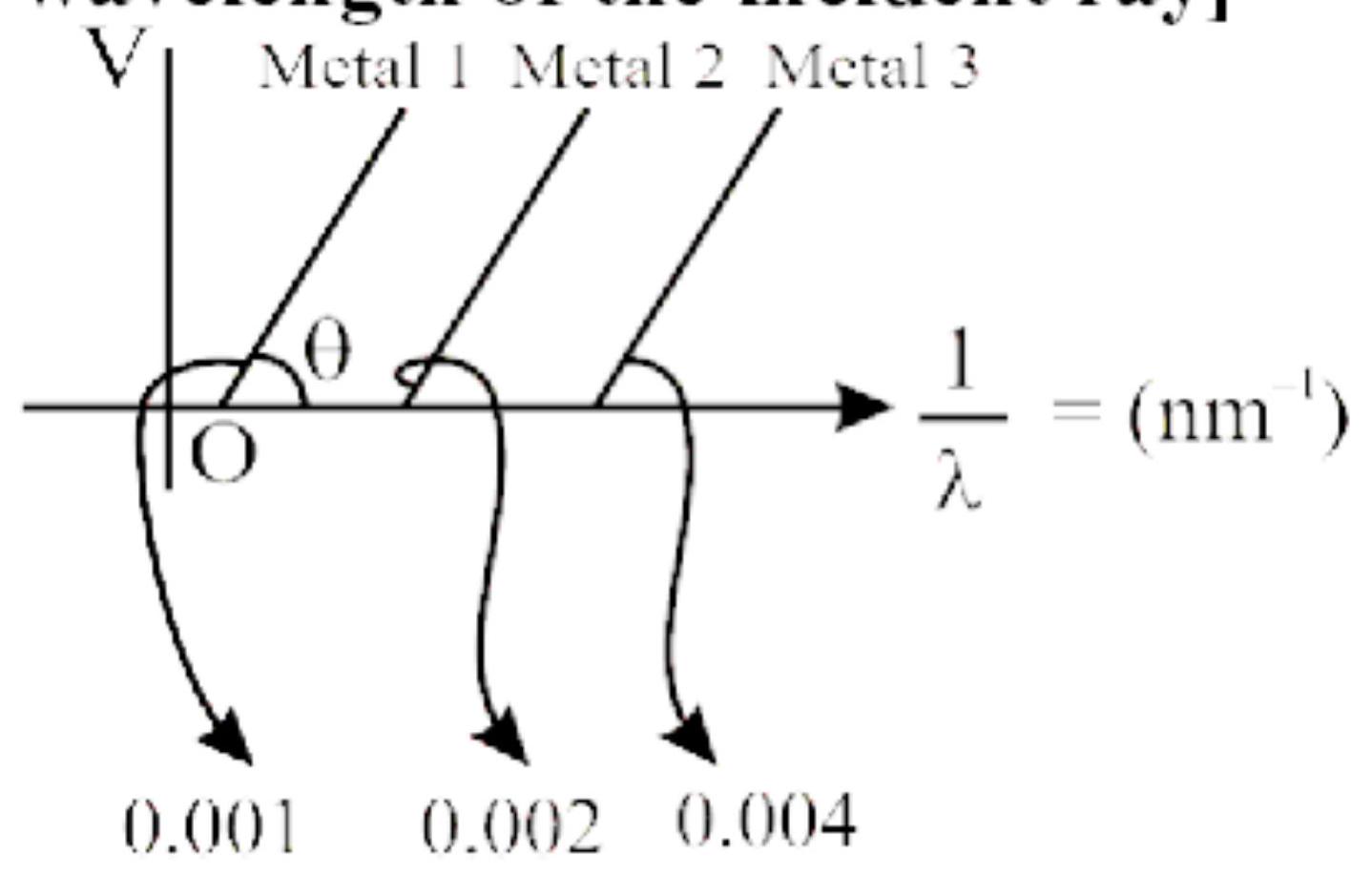
(I) Ratio of work functions
(II) Ratio of work functions
(III)
(IV) The violet colour-light can eject photoelectrons from metals 2 and 3
142148
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequency
142147
The graph 
(I) Ratio of work functions
(II) Ratio of work functions
(III)
(IV) The violet colour-light can eject photoelectrons from metals 2 and 3
142148
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequency
142147
The graph 
(I) Ratio of work functions
(II) Ratio of work functions
(III)
(IV) The violet colour-light can eject photoelectrons from metals 2 and 3
142148
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequency
142147
The graph 
(I) Ratio of work functions
(II) Ratio of work functions
(III)
(IV) The violet colour-light can eject photoelectrons from metals 2 and 3
142148
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequency
