138680 A satellite moves in elliptical orbit about a planet. Its maximum and minimum velocities of satellites are $3 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ and $1 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ respectively. What is the minimum distance of satellite from planet is maximum distance if $4 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~km}$ ?
138684
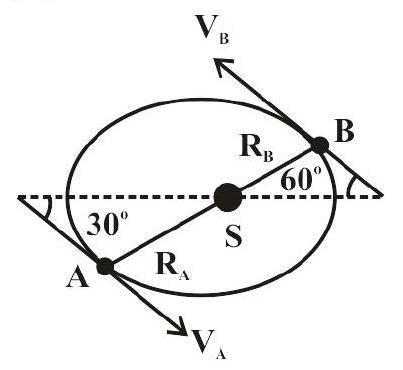
A planet is revolving around the Sun as shown in the figure. The radius vectors joining the Sun and the planet at point $A$ and $B$ are $90 \times$ $10^{6} \mathrm{~km}$ and $60 \times 10^{6} \mathrm{~km}$, respectively. The ratio of velocities of the planet at the points $A$ and $B$ when its velocities make angle $30^{\circ}$ and $60^{\circ}$ with major-axis of the orbit is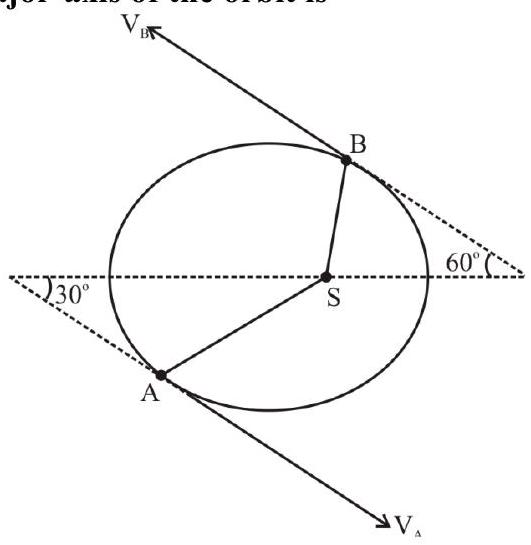
138680 A satellite moves in elliptical orbit about a planet. Its maximum and minimum velocities of satellites are $3 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ and $1 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ respectively. What is the minimum distance of satellite from planet is maximum distance if $4 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~km}$ ?
138684
A planet is revolving around the Sun as shown in the figure. The radius vectors joining the Sun and the planet at point $A$ and $B$ are $90 \times$ $10^{6} \mathrm{~km}$ and $60 \times 10^{6} \mathrm{~km}$, respectively. The ratio of velocities of the planet at the points $A$ and $B$ when its velocities make angle $30^{\circ}$ and $60^{\circ}$ with major-axis of the orbit is
138680 A satellite moves in elliptical orbit about a planet. Its maximum and minimum velocities of satellites are $3 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ and $1 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ respectively. What is the minimum distance of satellite from planet is maximum distance if $4 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~km}$ ?
138684
A planet is revolving around the Sun as shown in the figure. The radius vectors joining the Sun and the planet at point $A$ and $B$ are $90 \times$ $10^{6} \mathrm{~km}$ and $60 \times 10^{6} \mathrm{~km}$, respectively. The ratio of velocities of the planet at the points $A$ and $B$ when its velocities make angle $30^{\circ}$ and $60^{\circ}$ with major-axis of the orbit is
138680 A satellite moves in elliptical orbit about a planet. Its maximum and minimum velocities of satellites are $3 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ and $1 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ respectively. What is the minimum distance of satellite from planet is maximum distance if $4 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~km}$ ?
138684
A planet is revolving around the Sun as shown in the figure. The radius vectors joining the Sun and the planet at point $A$ and $B$ are $90 \times$ $10^{6} \mathrm{~km}$ and $60 \times 10^{6} \mathrm{~km}$, respectively. The ratio of velocities of the planet at the points $A$ and $B$ when its velocities make angle $30^{\circ}$ and $60^{\circ}$ with major-axis of the orbit is
138680 A satellite moves in elliptical orbit about a planet. Its maximum and minimum velocities of satellites are $3 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ and $1 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ respectively. What is the minimum distance of satellite from planet is maximum distance if $4 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~km}$ ?
138684
A planet is revolving around the Sun as shown in the figure. The radius vectors joining the Sun and the planet at point $A$ and $B$ are $90 \times$ $10^{6} \mathrm{~km}$ and $60 \times 10^{6} \mathrm{~km}$, respectively. The ratio of velocities of the planet at the points $A$ and $B$ when its velocities make angle $30^{\circ}$ and $60^{\circ}$ with major-axis of the orbit is