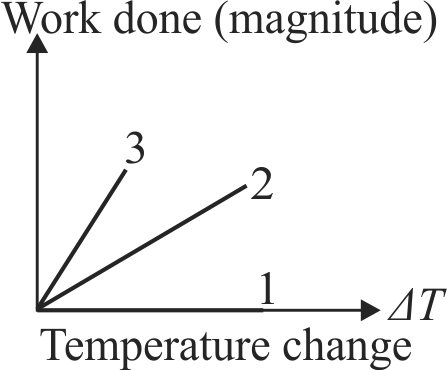
371495 Consider two containers \(A\) and \(B\) containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container \(A\) is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container \(B\) is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in \(B\) to that of gas in \(A\) is
371496 A perfect gas goes from state \(A\) to state \(B\) by absorbing \(8 \times {10^5}\;J\) of heat and doing \(6.5 \times {10^5}\;J\) of external work. It is now transferred between the same two states in another process in which it absorbs \({10^5}\;J\) of heat. In the second process,
371495 Consider two containers \(A\) and \(B\) containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container \(A\) is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container \(B\) is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in \(B\) to that of gas in \(A\) is
371496 A perfect gas goes from state \(A\) to state \(B\) by absorbing \(8 \times {10^5}\;J\) of heat and doing \(6.5 \times {10^5}\;J\) of external work. It is now transferred between the same two states in another process in which it absorbs \({10^5}\;J\) of heat. In the second process,
371495 Consider two containers \(A\) and \(B\) containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container \(A\) is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container \(B\) is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in \(B\) to that of gas in \(A\) is
371496 A perfect gas goes from state \(A\) to state \(B\) by absorbing \(8 \times {10^5}\;J\) of heat and doing \(6.5 \times {10^5}\;J\) of external work. It is now transferred between the same two states in another process in which it absorbs \({10^5}\;J\) of heat. In the second process,
371495 Consider two containers \(A\) and \(B\) containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container \(A\) is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container \(B\) is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in \(B\) to that of gas in \(A\) is
371496 A perfect gas goes from state \(A\) to state \(B\) by absorbing \(8 \times {10^5}\;J\) of heat and doing \(6.5 \times {10^5}\;J\) of external work. It is now transferred between the same two states in another process in which it absorbs \({10^5}\;J\) of heat. In the second process,
371495 Consider two containers \(A\) and \(B\) containing identical gases at the same pressure, volume and temperature. The gas in container \(A\) is compressed to half of its original volume isothermally while the gas in container \(B\) is compressed to half of its original value adiabatically. The ratio of final pressure of gas in \(B\) to that of gas in \(A\) is
371496 A perfect gas goes from state \(A\) to state \(B\) by absorbing \(8 \times {10^5}\;J\) of heat and doing \(6.5 \times {10^5}\;J\) of external work. It is now transferred between the same two states in another process in which it absorbs \({10^5}\;J\) of heat. In the second process,