371406
Two Carnot engines are operated in series between three reservoirs at temperatures \({T_1},\;{T_2}\) and \({T_3}\) respectively as shown in figure. First engine receives heat from first reservoir and rejects some amount of heat to the second reservoir. Second engine absorbs the heat rejected from first engine and rejects remaining amount of heat to the third reservoir at \({T_3}.\) Considering the work outputs of the two engines to be equal, calculate the temperature \({T_2}\) .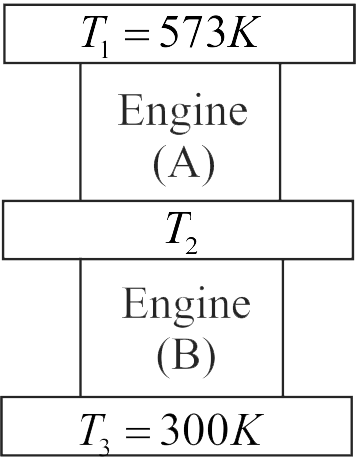
371406
Two Carnot engines are operated in series between three reservoirs at temperatures \({T_1},\;{T_2}\) and \({T_3}\) respectively as shown in figure. First engine receives heat from first reservoir and rejects some amount of heat to the second reservoir. Second engine absorbs the heat rejected from first engine and rejects remaining amount of heat to the third reservoir at \({T_3}.\) Considering the work outputs of the two engines to be equal, calculate the temperature \({T_2}\) .
371406
Two Carnot engines are operated in series between three reservoirs at temperatures \({T_1},\;{T_2}\) and \({T_3}\) respectively as shown in figure. First engine receives heat from first reservoir and rejects some amount of heat to the second reservoir. Second engine absorbs the heat rejected from first engine and rejects remaining amount of heat to the third reservoir at \({T_3}.\) Considering the work outputs of the two engines to be equal, calculate the temperature \({T_2}\) .
371406
Two Carnot engines are operated in series between three reservoirs at temperatures \({T_1},\;{T_2}\) and \({T_3}\) respectively as shown in figure. First engine receives heat from first reservoir and rejects some amount of heat to the second reservoir. Second engine absorbs the heat rejected from first engine and rejects remaining amount of heat to the third reservoir at \({T_3}.\) Considering the work outputs of the two engines to be equal, calculate the temperature \({T_2}\) .
