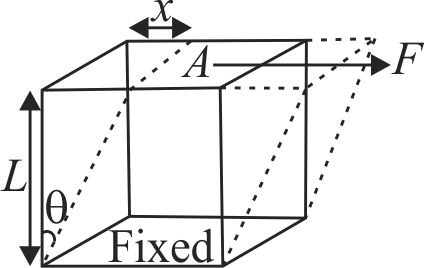
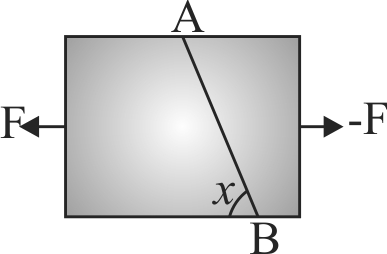
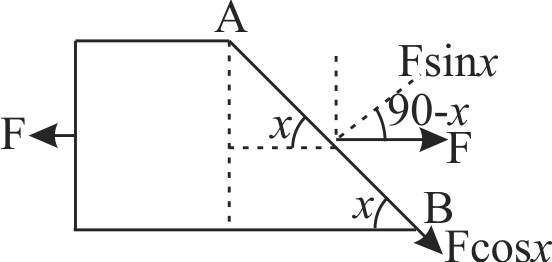
369767 A metal cube of side length \(8.0\;cm\) has its upper surface displaced with respect to the bottom by \(0.10\;mm\) when a tangential force of \(4 \times {10^9}\;N\) is applied at the top with bottom surface fixed. The rigidity modulus of the material of the cube is
369767 A metal cube of side length \(8.0\;cm\) has its upper surface displaced with respect to the bottom by \(0.10\;mm\) when a tangential force of \(4 \times {10^9}\;N\) is applied at the top with bottom surface fixed. The rigidity modulus of the material of the cube is
369767 A metal cube of side length \(8.0\;cm\) has its upper surface displaced with respect to the bottom by \(0.10\;mm\) when a tangential force of \(4 \times {10^9}\;N\) is applied at the top with bottom surface fixed. The rigidity modulus of the material of the cube is
369767 A metal cube of side length \(8.0\;cm\) has its upper surface displaced with respect to the bottom by \(0.10\;mm\) when a tangential force of \(4 \times {10^9}\;N\) is applied at the top with bottom surface fixed. The rigidity modulus of the material of the cube is