355321
In the figure, pendulum bob on left side is pulled a side to a height \(h\) from its initial position. After it is released it collides with the right pendulum bob at rest, which is of same mass. After the collision, the two bobs stick together and rise to a height.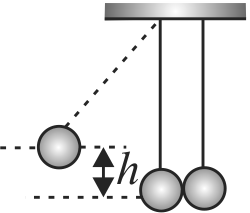
355322 A body of mass 2 \(kg\) moving with a velocity of 3 \(m/s\) collides head-on with a body of mass 1 \(kg\) moving in opposite direction with a velocity of 4 \(m/s\). After collision two bodies stick together and moves with a common velocity which in \(m/s\) is equal to
355321
In the figure, pendulum bob on left side is pulled a side to a height \(h\) from its initial position. After it is released it collides with the right pendulum bob at rest, which is of same mass. After the collision, the two bobs stick together and rise to a height.
355322 A body of mass 2 \(kg\) moving with a velocity of 3 \(m/s\) collides head-on with a body of mass 1 \(kg\) moving in opposite direction with a velocity of 4 \(m/s\). After collision two bodies stick together and moves with a common velocity which in \(m/s\) is equal to
355321
In the figure, pendulum bob on left side is pulled a side to a height \(h\) from its initial position. After it is released it collides with the right pendulum bob at rest, which is of same mass. After the collision, the two bobs stick together and rise to a height.
355322 A body of mass 2 \(kg\) moving with a velocity of 3 \(m/s\) collides head-on with a body of mass 1 \(kg\) moving in opposite direction with a velocity of 4 \(m/s\). After collision two bodies stick together and moves with a common velocity which in \(m/s\) is equal to
355321
In the figure, pendulum bob on left side is pulled a side to a height \(h\) from its initial position. After it is released it collides with the right pendulum bob at rest, which is of same mass. After the collision, the two bobs stick together and rise to a height.
355322 A body of mass 2 \(kg\) moving with a velocity of 3 \(m/s\) collides head-on with a body of mass 1 \(kg\) moving in opposite direction with a velocity of 4 \(m/s\). After collision two bodies stick together and moves with a common velocity which in \(m/s\) is equal to
