355219
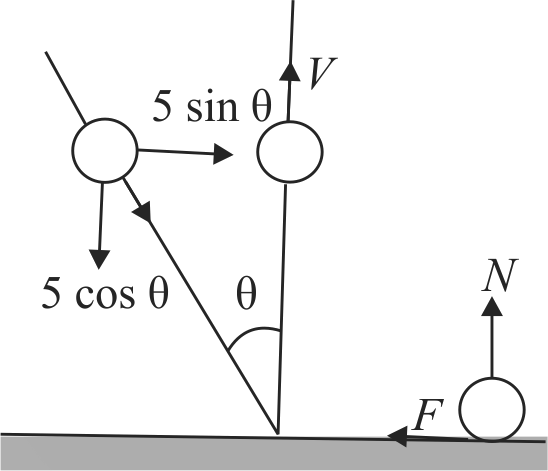
A ball of mass 1 \(kg\) moving with a velocity of \(5 {~m} / {s}\) collides elastically with rough ground at an angle \(\theta\) with the vertical as shown in figure. What can be the minimum coefficient of friction if ball rebounds vertically after collision?
(\({\rm{Given}}\,\,\tan \theta = 2\))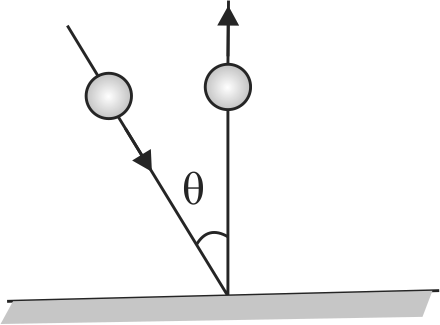
355219
A ball of mass 1 \(kg\) moving with a velocity of \(5 {~m} / {s}\) collides elastically with rough ground at an angle \(\theta\) with the vertical as shown in figure. What can be the minimum coefficient of friction if ball rebounds vertically after collision?
(\({\rm{Given}}\,\,\tan \theta = 2\))
355219
A ball of mass 1 \(kg\) moving with a velocity of \(5 {~m} / {s}\) collides elastically with rough ground at an angle \(\theta\) with the vertical as shown in figure. What can be the minimum coefficient of friction if ball rebounds vertically after collision?
(\({\rm{Given}}\,\,\tan \theta = 2\))
355219
A ball of mass 1 \(kg\) moving with a velocity of \(5 {~m} / {s}\) collides elastically with rough ground at an angle \(\theta\) with the vertical as shown in figure. What can be the minimum coefficient of friction if ball rebounds vertically after collision?
(\({\rm{Given}}\,\,\tan \theta = 2\))
355219
A ball of mass 1 \(kg\) moving with a velocity of \(5 {~m} / {s}\) collides elastically with rough ground at an angle \(\theta\) with the vertical as shown in figure. What can be the minimum coefficient of friction if ball rebounds vertically after collision?
(\({\rm{Given}}\,\,\tan \theta = 2\))