Explanation:
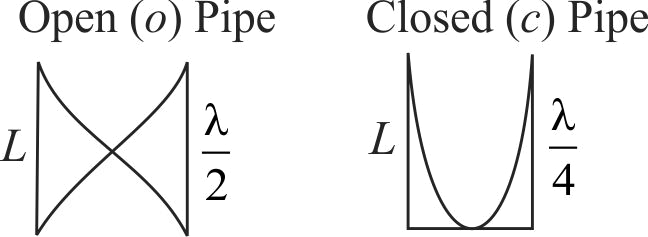
\(L = \frac{\lambda }{2}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,L = \frac{\lambda }{4}\)
\(\lambda = 2\,L\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\lambda = 4L\)
\({f_0} = \frac{\upsilon }{\lambda }\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{f_c} = \frac{\upsilon }{\lambda }\)
\( \Rightarrow {f_0} = \frac{\upsilon }{{2L}}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,(1)\)
\( \Rightarrow {f_c} = \frac{\upsilon }{{4L}}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,(2)\)
\( \Rightarrow \frac{{{f_0}}}{{{f_c}}} = \frac{\upsilon }{{2\,L}} \times \frac{{4\,L}}{\upsilon }\)
\( \Rightarrow \frac{{{f_0}}}{{{f_c}}} = \frac{2}{1}\)
Correct option is (1).