359190
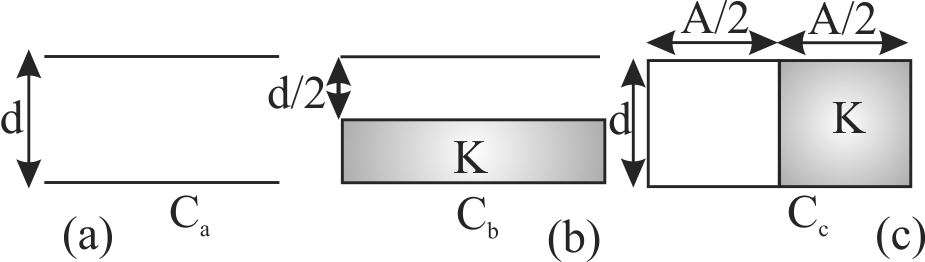
Four identical plates 1, 2, 3 and 4 placed parallel to each other at equal distance as shown in the figure. Plates 1 and 4 are joined together and the space between 2 and 3 is filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant \(k = 2\). The capacitance of the system between 1 and 3 & 2 and 4 are \({C_{13}}\) and \({C_{24}}\) respectively. The ratio \(\frac{{{C_{13}}}}{{{C_{24}}}}\) is :
359190
Four identical plates 1, 2, 3 and 4 placed parallel to each other at equal distance as shown in the figure. Plates 1 and 4 are joined together and the space between 2 and 3 is filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant \(k = 2\). The capacitance of the system between 1 and 3 & 2 and 4 are \({C_{13}}\) and \({C_{24}}\) respectively. The ratio \(\frac{{{C_{13}}}}{{{C_{24}}}}\) is :
359190
Four identical plates 1, 2, 3 and 4 placed parallel to each other at equal distance as shown in the figure. Plates 1 and 4 are joined together and the space between 2 and 3 is filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant \(k = 2\). The capacitance of the system between 1 and 3 & 2 and 4 are \({C_{13}}\) and \({C_{24}}\) respectively. The ratio \(\frac{{{C_{13}}}}{{{C_{24}}}}\) is :
359190
Four identical plates 1, 2, 3 and 4 placed parallel to each other at equal distance as shown in the figure. Plates 1 and 4 are joined together and the space between 2 and 3 is filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant \(k = 2\). The capacitance of the system between 1 and 3 & 2 and 4 are \({C_{13}}\) and \({C_{24}}\) respectively. The ratio \(\frac{{{C_{13}}}}{{{C_{24}}}}\) is :