365621
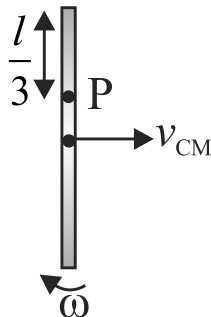
A thin uniform rod of mass \(m\) and length \(l\) is kept on a smooth horizontal surface such that it can move freely. At what distance from centre of rod should a particle of mass \(m\) strike on the rod such that the point \(\mathrm{P}\) at a distance \(l /\) 3 from the end of the rod is instantaneously at rest just after the elastic collision?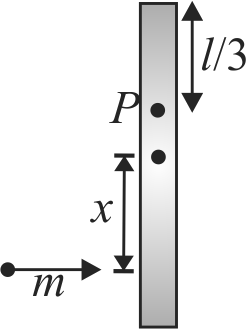
365622
A solid sphere of mass \(M\) and radius \(R\) is placed on a rough horizontal surface. It is struck by a horizontal cue stick at a height \(h\) above the surface. The value of \(h\) so that the sphere performs pure rolling motion immediately after it has been struck is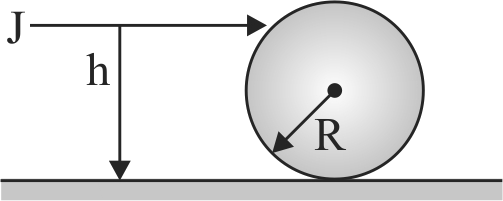
365623
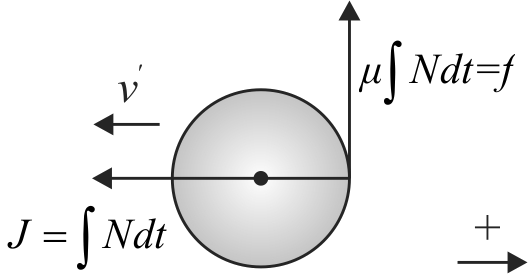
A uniform solid sphere of radius \(r\) is rolling on a smooth horizontal surface with velocity \(v\) and angular velocity \(\omega(v=\omega r)\). The sphere collides with the wall as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between the sphere and the edge \(\mu=1 / 5\). Just after the collision the angular velocity of the sphere becomes zero. The linear velocity of the sphere just after the collision is equal to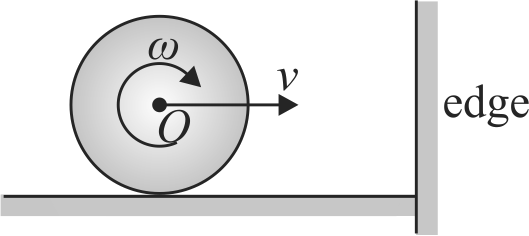
365621
A thin uniform rod of mass \(m\) and length \(l\) is kept on a smooth horizontal surface such that it can move freely. At what distance from centre of rod should a particle of mass \(m\) strike on the rod such that the point \(\mathrm{P}\) at a distance \(l /\) 3 from the end of the rod is instantaneously at rest just after the elastic collision?
365622
A solid sphere of mass \(M\) and radius \(R\) is placed on a rough horizontal surface. It is struck by a horizontal cue stick at a height \(h\) above the surface. The value of \(h\) so that the sphere performs pure rolling motion immediately after it has been struck is
365623
A uniform solid sphere of radius \(r\) is rolling on a smooth horizontal surface with velocity \(v\) and angular velocity \(\omega(v=\omega r)\). The sphere collides with the wall as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between the sphere and the edge \(\mu=1 / 5\). Just after the collision the angular velocity of the sphere becomes zero. The linear velocity of the sphere just after the collision is equal to
365621
A thin uniform rod of mass \(m\) and length \(l\) is kept on a smooth horizontal surface such that it can move freely. At what distance from centre of rod should a particle of mass \(m\) strike on the rod such that the point \(\mathrm{P}\) at a distance \(l /\) 3 from the end of the rod is instantaneously at rest just after the elastic collision?
365622
A solid sphere of mass \(M\) and radius \(R\) is placed on a rough horizontal surface. It is struck by a horizontal cue stick at a height \(h\) above the surface. The value of \(h\) so that the sphere performs pure rolling motion immediately after it has been struck is
365623
A uniform solid sphere of radius \(r\) is rolling on a smooth horizontal surface with velocity \(v\) and angular velocity \(\omega(v=\omega r)\). The sphere collides with the wall as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between the sphere and the edge \(\mu=1 / 5\). Just after the collision the angular velocity of the sphere becomes zero. The linear velocity of the sphere just after the collision is equal to
365621
A thin uniform rod of mass \(m\) and length \(l\) is kept on a smooth horizontal surface such that it can move freely. At what distance from centre of rod should a particle of mass \(m\) strike on the rod such that the point \(\mathrm{P}\) at a distance \(l /\) 3 from the end of the rod is instantaneously at rest just after the elastic collision?
365622
A solid sphere of mass \(M\) and radius \(R\) is placed on a rough horizontal surface. It is struck by a horizontal cue stick at a height \(h\) above the surface. The value of \(h\) so that the sphere performs pure rolling motion immediately after it has been struck is
365623
A uniform solid sphere of radius \(r\) is rolling on a smooth horizontal surface with velocity \(v\) and angular velocity \(\omega(v=\omega r)\). The sphere collides with the wall as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between the sphere and the edge \(\mu=1 / 5\). Just after the collision the angular velocity of the sphere becomes zero. The linear velocity of the sphere just after the collision is equal to