364931
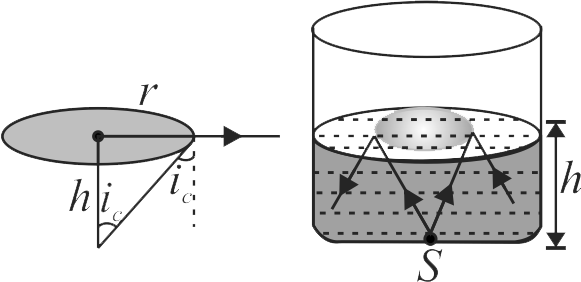
A point source of light \({S}\) is placed at the bottom of a vessel containing a liquid of refractive index \({5 / 3}\). A person is viewing the source from above the surface. There is an opaque disc \({D}\) of radius \(1\,cm\) floating on the surface of the liquid. The centre of the disc lies vertically above the source. The liquid from the vessel is gradually drained out through a tap. The maximum height of the liquid for which the source cannot be seen at all from above is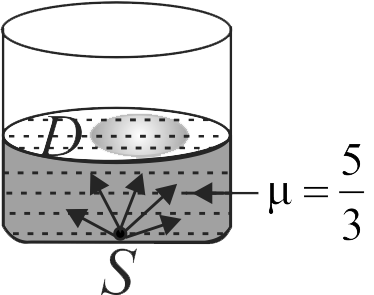
364931
A point source of light \({S}\) is placed at the bottom of a vessel containing a liquid of refractive index \({5 / 3}\). A person is viewing the source from above the surface. There is an opaque disc \({D}\) of radius \(1\,cm\) floating on the surface of the liquid. The centre of the disc lies vertically above the source. The liquid from the vessel is gradually drained out through a tap. The maximum height of the liquid for which the source cannot be seen at all from above is
364931
A point source of light \({S}\) is placed at the bottom of a vessel containing a liquid of refractive index \({5 / 3}\). A person is viewing the source from above the surface. There is an opaque disc \({D}\) of radius \(1\,cm\) floating on the surface of the liquid. The centre of the disc lies vertically above the source. The liquid from the vessel is gradually drained out through a tap. The maximum height of the liquid for which the source cannot be seen at all from above is
364931
A point source of light \({S}\) is placed at the bottom of a vessel containing a liquid of refractive index \({5 / 3}\). A person is viewing the source from above the surface. There is an opaque disc \({D}\) of radius \(1\,cm\) floating on the surface of the liquid. The centre of the disc lies vertically above the source. The liquid from the vessel is gradually drained out through a tap. The maximum height of the liquid for which the source cannot be seen at all from above is