364850
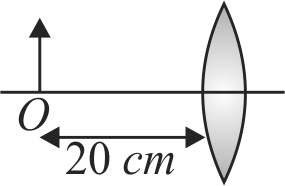
Figure given below shows a beam of light converging at point \({\rm{P}}\). When a concave lens of focal length \({\rm{16}}\;{\rm{cm}}\) is introduced in the path of the beam at a place \(O\) shown by dotted line such that \(OP\) becomes the axis of the lens, the beam converges at a distance \(x\) from the lens. The value \(x\) will be equal to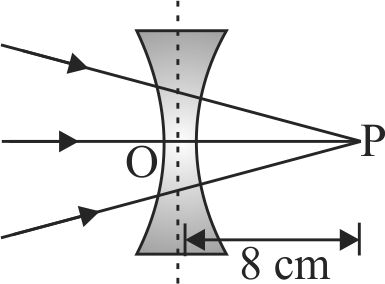
364850
Figure given below shows a beam of light converging at point \({\rm{P}}\). When a concave lens of focal length \({\rm{16}}\;{\rm{cm}}\) is introduced in the path of the beam at a place \(O\) shown by dotted line such that \(OP\) becomes the axis of the lens, the beam converges at a distance \(x\) from the lens. The value \(x\) will be equal to
364850
Figure given below shows a beam of light converging at point \({\rm{P}}\). When a concave lens of focal length \({\rm{16}}\;{\rm{cm}}\) is introduced in the path of the beam at a place \(O\) shown by dotted line such that \(OP\) becomes the axis of the lens, the beam converges at a distance \(x\) from the lens. The value \(x\) will be equal to
364850
Figure given below shows a beam of light converging at point \({\rm{P}}\). When a concave lens of focal length \({\rm{16}}\;{\rm{cm}}\) is introduced in the path of the beam at a place \(O\) shown by dotted line such that \(OP\) becomes the axis of the lens, the beam converges at a distance \(x\) from the lens. The value \(x\) will be equal to
364850
Figure given below shows a beam of light converging at point \({\rm{P}}\). When a concave lens of focal length \({\rm{16}}\;{\rm{cm}}\) is introduced in the path of the beam at a place \(O\) shown by dotted line such that \(OP\) becomes the axis of the lens, the beam converges at a distance \(x\) from the lens. The value \(x\) will be equal to