364803
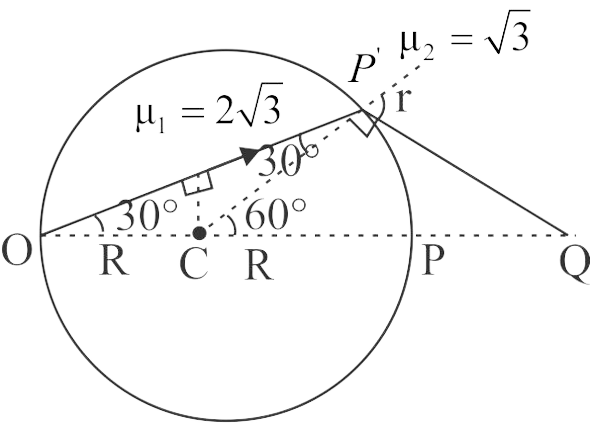
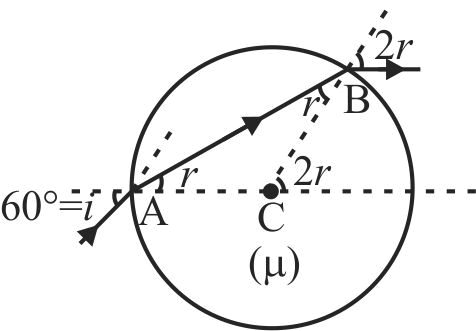
A point source \({\rm{O}}\) kept at distance of \(2R{\rm{ }}\) from pole \({\rm{ P}}\) of a concave interface having radius of curvature \(R\) emits a beam at an angle of \(30^\circ \) to the principle axis \({\rm{ PO}}\). The distance of the image of point source \({\rm{O}}\) from pole \({\rm{ P }}\)is: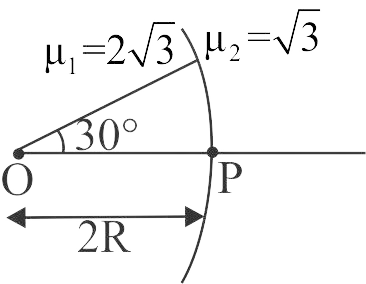
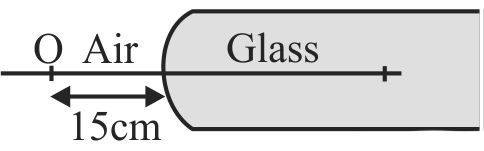
364806 One end of a cylindrical glass rod \(\left( {\mu = 1.5} \right)\) is given the shape of a concave refracing surface of radius \(10\;cm\) . An air bubble is situated in the glass rod at a point on its axis such that it appears to be at distance \(10\;cm\) from the surface and inside glass when seen from the other medium. Find the actual location of air bubble, from the surface.
364803
A point source \({\rm{O}}\) kept at distance of \(2R{\rm{ }}\) from pole \({\rm{ P}}\) of a concave interface having radius of curvature \(R\) emits a beam at an angle of \(30^\circ \) to the principle axis \({\rm{ PO}}\). The distance of the image of point source \({\rm{O}}\) from pole \({\rm{ P }}\)is:
364806 One end of a cylindrical glass rod \(\left( {\mu = 1.5} \right)\) is given the shape of a concave refracing surface of radius \(10\;cm\) . An air bubble is situated in the glass rod at a point on its axis such that it appears to be at distance \(10\;cm\) from the surface and inside glass when seen from the other medium. Find the actual location of air bubble, from the surface.
364803
A point source \({\rm{O}}\) kept at distance of \(2R{\rm{ }}\) from pole \({\rm{ P}}\) of a concave interface having radius of curvature \(R\) emits a beam at an angle of \(30^\circ \) to the principle axis \({\rm{ PO}}\). The distance of the image of point source \({\rm{O}}\) from pole \({\rm{ P }}\)is:
364806 One end of a cylindrical glass rod \(\left( {\mu = 1.5} \right)\) is given the shape of a concave refracing surface of radius \(10\;cm\) . An air bubble is situated in the glass rod at a point on its axis such that it appears to be at distance \(10\;cm\) from the surface and inside glass when seen from the other medium. Find the actual location of air bubble, from the surface.
364803
A point source \({\rm{O}}\) kept at distance of \(2R{\rm{ }}\) from pole \({\rm{ P}}\) of a concave interface having radius of curvature \(R\) emits a beam at an angle of \(30^\circ \) to the principle axis \({\rm{ PO}}\). The distance of the image of point source \({\rm{O}}\) from pole \({\rm{ P }}\)is:
364806 One end of a cylindrical glass rod \(\left( {\mu = 1.5} \right)\) is given the shape of a concave refracing surface of radius \(10\;cm\) . An air bubble is situated in the glass rod at a point on its axis such that it appears to be at distance \(10\;cm\) from the surface and inside glass when seen from the other medium. Find the actual location of air bubble, from the surface.
364803
A point source \({\rm{O}}\) kept at distance of \(2R{\rm{ }}\) from pole \({\rm{ P}}\) of a concave interface having radius of curvature \(R\) emits a beam at an angle of \(30^\circ \) to the principle axis \({\rm{ PO}}\). The distance of the image of point source \({\rm{O}}\) from pole \({\rm{ P }}\)is:
364806 One end of a cylindrical glass rod \(\left( {\mu = 1.5} \right)\) is given the shape of a concave refracing surface of radius \(10\;cm\) . An air bubble is situated in the glass rod at a point on its axis such that it appears to be at distance \(10\;cm\) from the surface and inside glass when seen from the other medium. Find the actual location of air bubble, from the surface.