358483
Wire \({P Q}\) with negligible resistance slides on the three rails with \({5 {~cm} / {sec}}\). If the current in \({10\,\, \Omega}\) resistance when switch \({S}\) is connected to position 1 is \({i_{1}}\) and when the switch is at position 2 the current becomes \({i_{2}}\). Find the ratio \({\dfrac{i_{1}}{i_{2}}}\).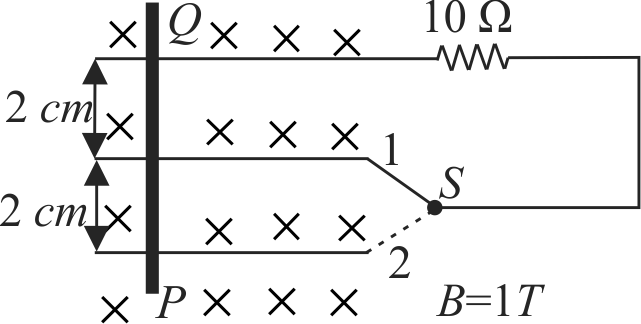
358484
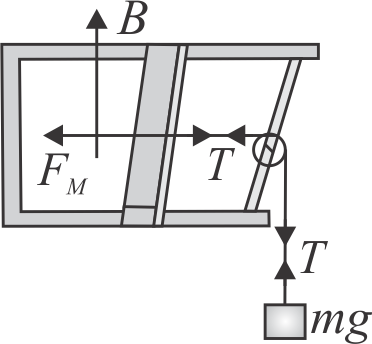
A pair of parallel horizontal conducting rails of negligible resistance shorted at one end is fixed on a table. The distance between the rails is \({l}\). A conducting massless rod of resistance \({R}\) can slide on the rails frictionlessly. The rod is tied to a massless string which passes over a pulley fixed to the edge of the table. A mass \({m}\), tied to the other end of the string, hangs vertically. A constant magnetic field \({B}\) exists perpendicular to the table. If the system is released from rest, calculate the acceleration of the mass at the instant when the velocity of the rod is half the terminal velocity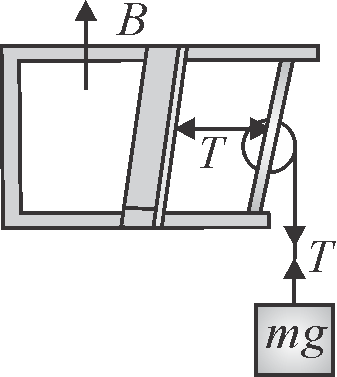
358486
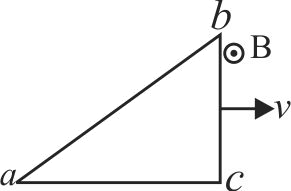
One conducting \(U\) tube can slide inside another as shown in figure, maintaining electrical contacts between the tubes. The magnetic field \(B\) is perpendicular to the plane of the figure. If each tube moves towards the other at a constant speed \(v\) then the emf induced in the circuit in terms of \(B, l\) and \(v\) where \(l\) is the width of each tube, will be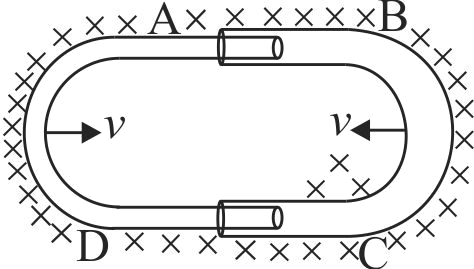
358483
Wire \({P Q}\) with negligible resistance slides on the three rails with \({5 {~cm} / {sec}}\). If the current in \({10\,\, \Omega}\) resistance when switch \({S}\) is connected to position 1 is \({i_{1}}\) and when the switch is at position 2 the current becomes \({i_{2}}\). Find the ratio \({\dfrac{i_{1}}{i_{2}}}\).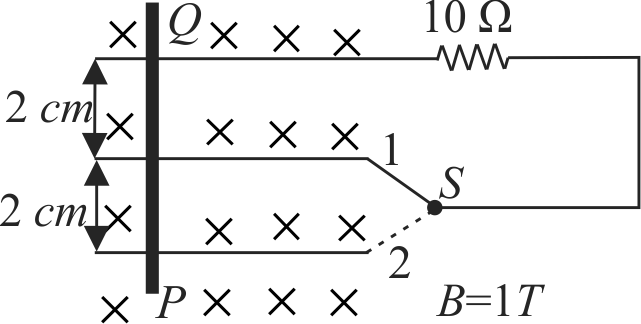
358484
A pair of parallel horizontal conducting rails of negligible resistance shorted at one end is fixed on a table. The distance between the rails is \({l}\). A conducting massless rod of resistance \({R}\) can slide on the rails frictionlessly. The rod is tied to a massless string which passes over a pulley fixed to the edge of the table. A mass \({m}\), tied to the other end of the string, hangs vertically. A constant magnetic field \({B}\) exists perpendicular to the table. If the system is released from rest, calculate the acceleration of the mass at the instant when the velocity of the rod is half the terminal velocity
358486
One conducting \(U\) tube can slide inside another as shown in figure, maintaining electrical contacts between the tubes. The magnetic field \(B\) is perpendicular to the plane of the figure. If each tube moves towards the other at a constant speed \(v\) then the emf induced in the circuit in terms of \(B, l\) and \(v\) where \(l\) is the width of each tube, will be
358483
Wire \({P Q}\) with negligible resistance slides on the three rails with \({5 {~cm} / {sec}}\). If the current in \({10\,\, \Omega}\) resistance when switch \({S}\) is connected to position 1 is \({i_{1}}\) and when the switch is at position 2 the current becomes \({i_{2}}\). Find the ratio \({\dfrac{i_{1}}{i_{2}}}\).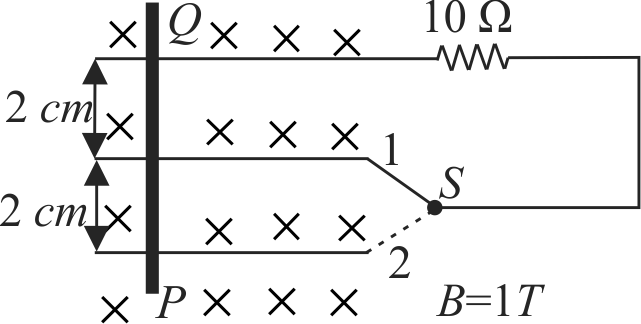
358484
A pair of parallel horizontal conducting rails of negligible resistance shorted at one end is fixed on a table. The distance between the rails is \({l}\). A conducting massless rod of resistance \({R}\) can slide on the rails frictionlessly. The rod is tied to a massless string which passes over a pulley fixed to the edge of the table. A mass \({m}\), tied to the other end of the string, hangs vertically. A constant magnetic field \({B}\) exists perpendicular to the table. If the system is released from rest, calculate the acceleration of the mass at the instant when the velocity of the rod is half the terminal velocity
358486
One conducting \(U\) tube can slide inside another as shown in figure, maintaining electrical contacts between the tubes. The magnetic field \(B\) is perpendicular to the plane of the figure. If each tube moves towards the other at a constant speed \(v\) then the emf induced in the circuit in terms of \(B, l\) and \(v\) where \(l\) is the width of each tube, will be
358483
Wire \({P Q}\) with negligible resistance slides on the three rails with \({5 {~cm} / {sec}}\). If the current in \({10\,\, \Omega}\) resistance when switch \({S}\) is connected to position 1 is \({i_{1}}\) and when the switch is at position 2 the current becomes \({i_{2}}\). Find the ratio \({\dfrac{i_{1}}{i_{2}}}\).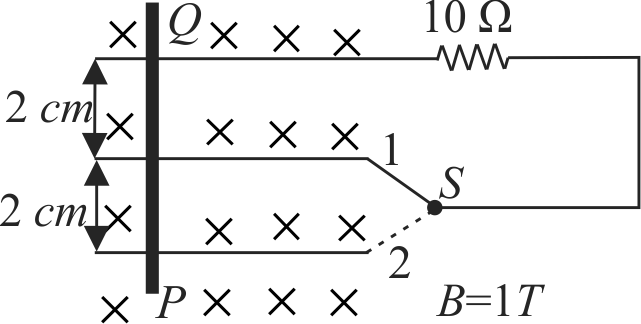
358484
A pair of parallel horizontal conducting rails of negligible resistance shorted at one end is fixed on a table. The distance between the rails is \({l}\). A conducting massless rod of resistance \({R}\) can slide on the rails frictionlessly. The rod is tied to a massless string which passes over a pulley fixed to the edge of the table. A mass \({m}\), tied to the other end of the string, hangs vertically. A constant magnetic field \({B}\) exists perpendicular to the table. If the system is released from rest, calculate the acceleration of the mass at the instant when the velocity of the rod is half the terminal velocity
358486
One conducting \(U\) tube can slide inside another as shown in figure, maintaining electrical contacts between the tubes. The magnetic field \(B\) is perpendicular to the plane of the figure. If each tube moves towards the other at a constant speed \(v\) then the emf induced in the circuit in terms of \(B, l\) and \(v\) where \(l\) is the width of each tube, will be