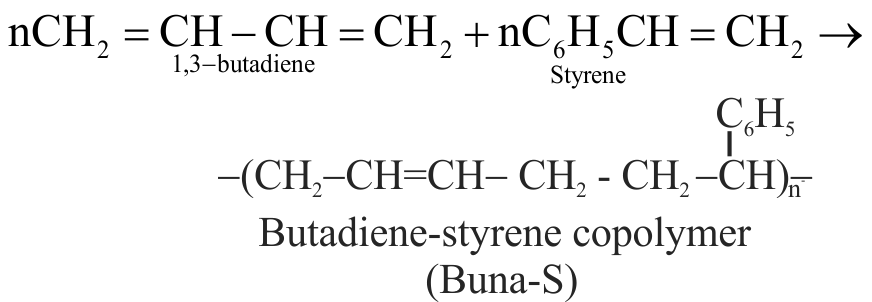Explanation:
The repeated addition of monomer molecules possessing double or triple bonds results in the formation of addition polymers. E.g., formation of polythene from ethene. When this addition involves the single monomeric unit, the polymers thus formed are called homopolymers like polythene.
\(\mathop {{\text{nC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}}\limits_{{\text{ethene}}} \xrightarrow{{{\text{Polymerisation}}}}\mathop {{\text{ - (C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{n}}}{\text{ - }}}\limits_{{\text{Polythene}}\,{\text{(hom}}\,{\text{opolymer)}}} \)
And when the addition polymers are formed from two different monomeric species, they are called copolymers like buna-N, buna-S etc.