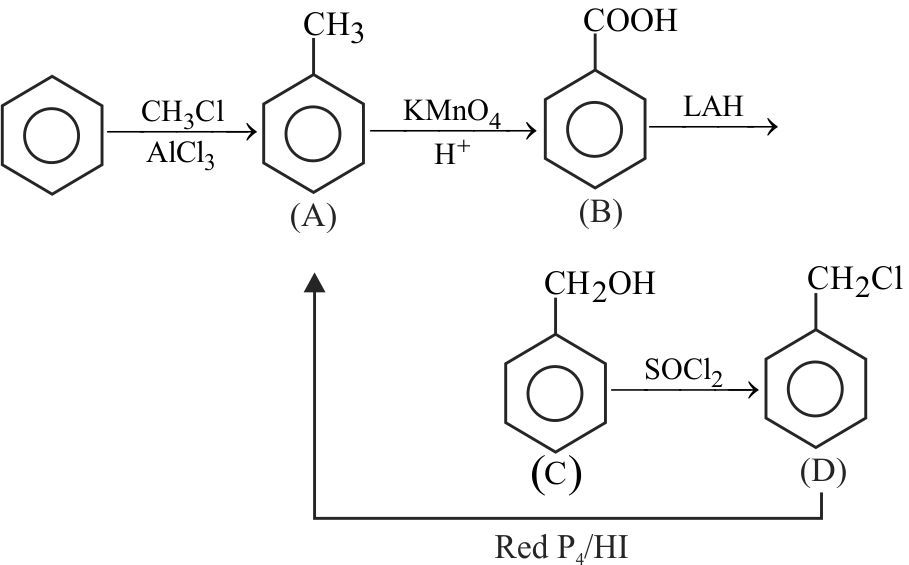
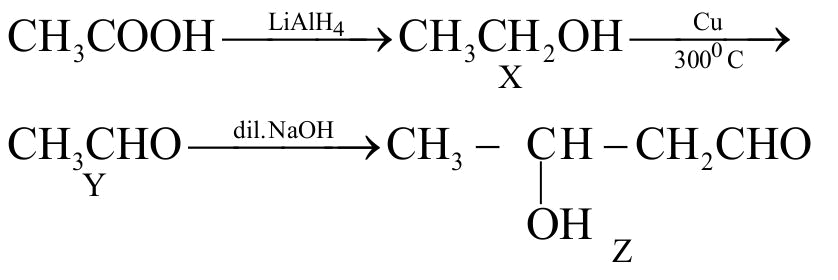
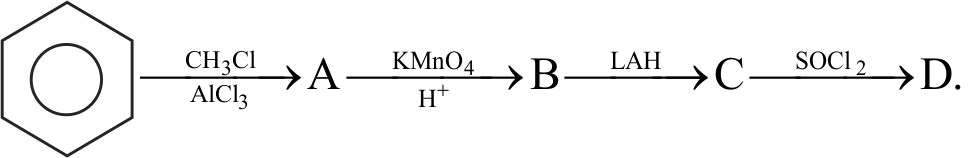323770
\(\begin{gathered}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}}}{\text{X}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{30}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\mkern 1mu} {\text{C}}}]{{{\text{Cu}}}}{\text{Y}}{\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} \hfill \\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\xrightarrow[{{\text{NaOH}}}]{{{\text{dilute}}}}{\text{Z}} \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \)
In the above reaction Z is
323771
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ - C}} \equiv {\text{C - }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\frac{{{\text{1}}{\text{.}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{/Cl}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}}}{{2 \cdot {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}}{\text{A + B}}\).
Product (A) forms polymer in liquid phase and forms dimer in Dry benzene. Product (B) gives \(\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{COOCH}_{3}\) when reacts with Methanol. The molecular weight difference between A & \(\mathrm{B}\) is
323770
\(\begin{gathered}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}}}{\text{X}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{30}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\mkern 1mu} {\text{C}}}]{{{\text{Cu}}}}{\text{Y}}{\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} \hfill \\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\xrightarrow[{{\text{NaOH}}}]{{{\text{dilute}}}}{\text{Z}} \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \)
In the above reaction Z is
323771
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ - C}} \equiv {\text{C - }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\frac{{{\text{1}}{\text{.}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{/Cl}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}}}{{2 \cdot {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}}{\text{A + B}}\).
Product (A) forms polymer in liquid phase and forms dimer in Dry benzene. Product (B) gives \(\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{COOCH}_{3}\) when reacts with Methanol. The molecular weight difference between A & \(\mathrm{B}\) is
323770
\(\begin{gathered}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}}}{\text{X}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{30}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\mkern 1mu} {\text{C}}}]{{{\text{Cu}}}}{\text{Y}}{\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} \hfill \\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\xrightarrow[{{\text{NaOH}}}]{{{\text{dilute}}}}{\text{Z}} \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \)
In the above reaction Z is
323771
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ - C}} \equiv {\text{C - }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\frac{{{\text{1}}{\text{.}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{/Cl}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}}}{{2 \cdot {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}}{\text{A + B}}\).
Product (A) forms polymer in liquid phase and forms dimer in Dry benzene. Product (B) gives \(\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{COOCH}_{3}\) when reacts with Methanol. The molecular weight difference between A & \(\mathrm{B}\) is
323770
\(\begin{gathered}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}}}{\text{X}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{30}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}{\mkern 1mu} {\text{C}}}]{{{\text{Cu}}}}{\text{Y}}{\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} \hfill \\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\xrightarrow[{{\text{NaOH}}}]{{{\text{dilute}}}}{\text{Z}} \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \)
In the above reaction Z is
323771
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ - C}} \equiv {\text{C - }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\frac{{{\text{1}}{\text{.}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{/Cl}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}}}{{2 \cdot {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}}{\text{A + B}}\).
Product (A) forms polymer in liquid phase and forms dimer in Dry benzene. Product (B) gives \(\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{COOCH}_{3}\) when reacts with Methanol. The molecular weight difference between A & \(\mathrm{B}\) is