322880
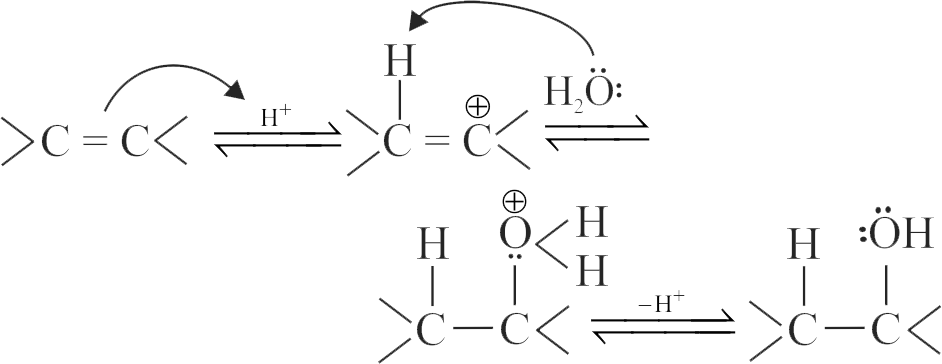
The acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes involves the following three steps:
I. Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
II. Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of
III. Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
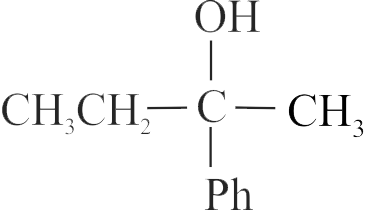
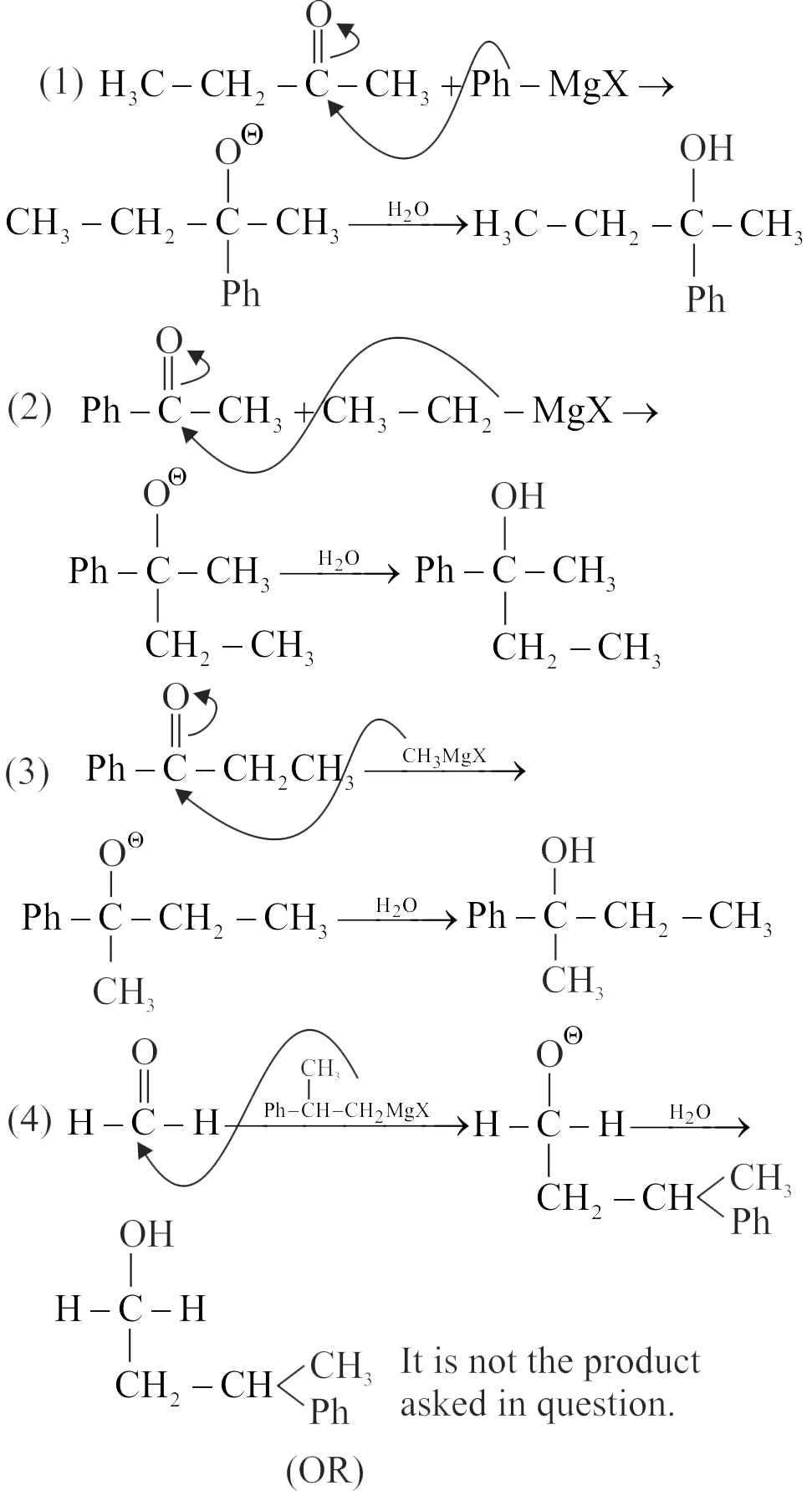
Identify the sequence for the mechanism of reaction in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.
322880
The acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes involves the following three steps:
I. Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
II. Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of
III. Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
Identify the sequence for the mechanism of reaction in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.
322880
The acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes involves the following three steps:
I. Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
II. Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of
III. Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
Identify the sequence for the mechanism of reaction in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.
322880
The acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes involves the following three steps:
I. Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
II. Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of
III. Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
Identify the sequence for the mechanism of reaction in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.
322880
The acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes involves the following three steps:
I. Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
II. Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of
III. Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
Identify the sequence for the mechanism of reaction in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.