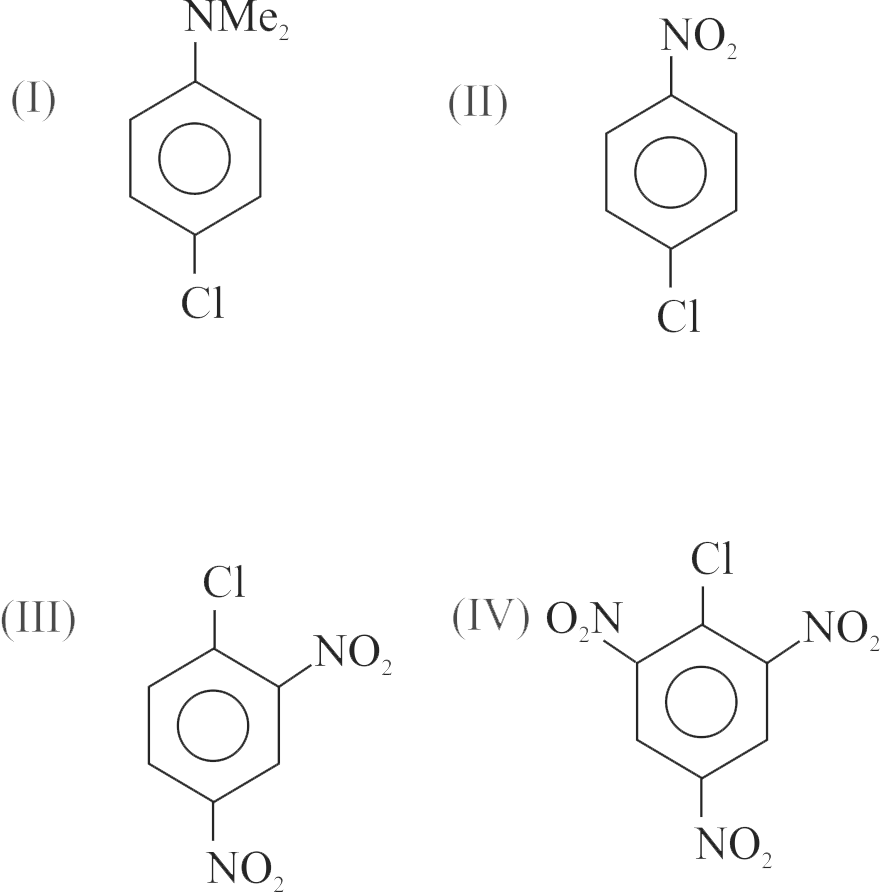
322826
Assertion :
4-Nitrochlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilie substitution readily more than chlorobenzene.
Reason :
Chlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilic substitution by elimination-addition mechanism while 4-nitrochlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilic substitution by addition-elimination mechanism.
322829
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution than alkyl halides.
Which of the following accounts for this?
(I) Due to resonance in aryl halides.
(II) In alkyl halides, carbon atom in \({\mathrm{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{X}}}\) bond is \({\mathrm{\mathrm{sp}^{2}}}\) hybridized whereas in aryl halides carbon atom in \({\mathrm{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{X}}}\) bond is \({\mathrm{\mathrm{sp}^{3}}}\) hybridized.
(III) Due to stability of phenyl cation.
(IV)Due to possible repulsion there are less chances of nucleophile to approach electron rich arenes.
322826
Assertion :
4-Nitrochlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilie substitution readily more than chlorobenzene.
Reason :
Chlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilic substitution by elimination-addition mechanism while 4-nitrochlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilic substitution by addition-elimination mechanism.
322829
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution than alkyl halides.
Which of the following accounts for this?
(I) Due to resonance in aryl halides.
(II) In alkyl halides, carbon atom in \({\mathrm{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{X}}}\) bond is \({\mathrm{\mathrm{sp}^{2}}}\) hybridized whereas in aryl halides carbon atom in \({\mathrm{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{X}}}\) bond is \({\mathrm{\mathrm{sp}^{3}}}\) hybridized.
(III) Due to stability of phenyl cation.
(IV)Due to possible repulsion there are less chances of nucleophile to approach electron rich arenes.
322826
Assertion :
4-Nitrochlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilie substitution readily more than chlorobenzene.
Reason :
Chlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilic substitution by elimination-addition mechanism while 4-nitrochlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilic substitution by addition-elimination mechanism.
322829
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution than alkyl halides.
Which of the following accounts for this?
(I) Due to resonance in aryl halides.
(II) In alkyl halides, carbon atom in \({\mathrm{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{X}}}\) bond is \({\mathrm{\mathrm{sp}^{2}}}\) hybridized whereas in aryl halides carbon atom in \({\mathrm{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{X}}}\) bond is \({\mathrm{\mathrm{sp}^{3}}}\) hybridized.
(III) Due to stability of phenyl cation.
(IV)Due to possible repulsion there are less chances of nucleophile to approach electron rich arenes.
322826
Assertion :
4-Nitrochlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilie substitution readily more than chlorobenzene.
Reason :
Chlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilic substitution by elimination-addition mechanism while 4-nitrochlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilic substitution by addition-elimination mechanism.
322829
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution than alkyl halides.
Which of the following accounts for this?
(I) Due to resonance in aryl halides.
(II) In alkyl halides, carbon atom in \({\mathrm{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{X}}}\) bond is \({\mathrm{\mathrm{sp}^{2}}}\) hybridized whereas in aryl halides carbon atom in \({\mathrm{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{X}}}\) bond is \({\mathrm{\mathrm{sp}^{3}}}\) hybridized.
(III) Due to stability of phenyl cation.
(IV)Due to possible repulsion there are less chances of nucleophile to approach electron rich arenes.