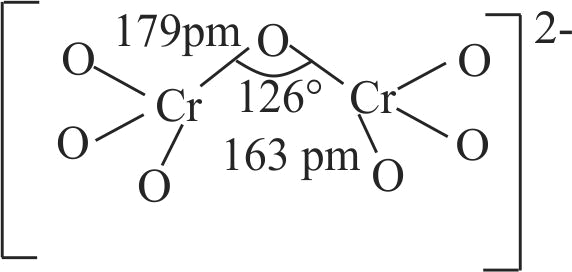
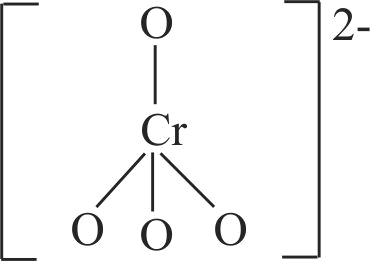
321277 When orange solution containing \(\mathrm{\mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}^{2-}}\) ion is treated with an alkali, a yellow solution is formed and when \(\mathrm{\mathrm{H}^{+}}\)ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen?
321277 When orange solution containing \(\mathrm{\mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}^{2-}}\) ion is treated with an alkali, a yellow solution is formed and when \(\mathrm{\mathrm{H}^{+}}\)ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen?
321277 When orange solution containing \(\mathrm{\mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}^{2-}}\) ion is treated with an alkali, a yellow solution is formed and when \(\mathrm{\mathrm{H}^{+}}\)ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen?
321277 When orange solution containing \(\mathrm{\mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}^{2-}}\) ion is treated with an alkali, a yellow solution is formed and when \(\mathrm{\mathrm{H}^{+}}\)ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen?