320274 The rate constant \({{\rm{k}}_{\rm{1}}}\) of a reaction is found to be double that of rate constant \({{\rm{k}}_{\rm{2}}}\) of another reaction. The relationship between corresponding activation energies of the two reactions at same temperature \(\left( {{{\rm{E}}_{\rm{1}}}} \right.\,\,{\rm{and}}\,\,{{\rm{E}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{)}}\) can be represented as
320277
The rate constant for the first order decomposition of the ethylene oxide into \(\mathrm{CH}_{4}\) and \(\mathrm{CO}\) is described by \(\log \mathrm{k}\left(\mathrm{s}^{-1}\right)=14.34-\dfrac{12.5 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~K}}{\mathrm{~T}}\)
Then the activation energy of the reaction is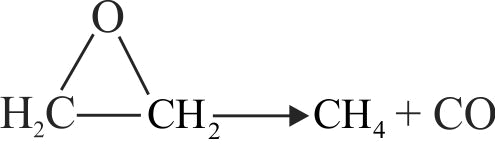
320274 The rate constant \({{\rm{k}}_{\rm{1}}}\) of a reaction is found to be double that of rate constant \({{\rm{k}}_{\rm{2}}}\) of another reaction. The relationship between corresponding activation energies of the two reactions at same temperature \(\left( {{{\rm{E}}_{\rm{1}}}} \right.\,\,{\rm{and}}\,\,{{\rm{E}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{)}}\) can be represented as
320277
The rate constant for the first order decomposition of the ethylene oxide into \(\mathrm{CH}_{4}\) and \(\mathrm{CO}\) is described by \(\log \mathrm{k}\left(\mathrm{s}^{-1}\right)=14.34-\dfrac{12.5 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~K}}{\mathrm{~T}}\)
Then the activation energy of the reaction is
320274 The rate constant \({{\rm{k}}_{\rm{1}}}\) of a reaction is found to be double that of rate constant \({{\rm{k}}_{\rm{2}}}\) of another reaction. The relationship between corresponding activation energies of the two reactions at same temperature \(\left( {{{\rm{E}}_{\rm{1}}}} \right.\,\,{\rm{and}}\,\,{{\rm{E}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{)}}\) can be represented as
320277
The rate constant for the first order decomposition of the ethylene oxide into \(\mathrm{CH}_{4}\) and \(\mathrm{CO}\) is described by \(\log \mathrm{k}\left(\mathrm{s}^{-1}\right)=14.34-\dfrac{12.5 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~K}}{\mathrm{~T}}\)
Then the activation energy of the reaction is
320274 The rate constant \({{\rm{k}}_{\rm{1}}}\) of a reaction is found to be double that of rate constant \({{\rm{k}}_{\rm{2}}}\) of another reaction. The relationship between corresponding activation energies of the two reactions at same temperature \(\left( {{{\rm{E}}_{\rm{1}}}} \right.\,\,{\rm{and}}\,\,{{\rm{E}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{)}}\) can be represented as
320277
The rate constant for the first order decomposition of the ethylene oxide into \(\mathrm{CH}_{4}\) and \(\mathrm{CO}\) is described by \(\log \mathrm{k}\left(\mathrm{s}^{-1}\right)=14.34-\dfrac{12.5 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~K}}{\mathrm{~T}}\)
Then the activation energy of the reaction is