320184
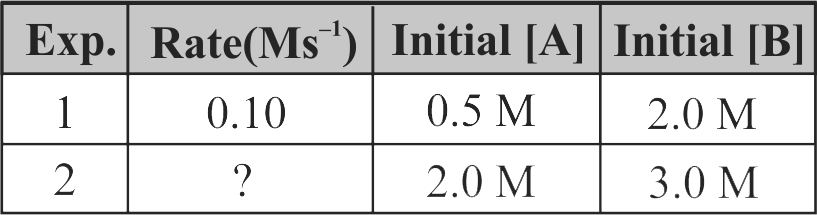
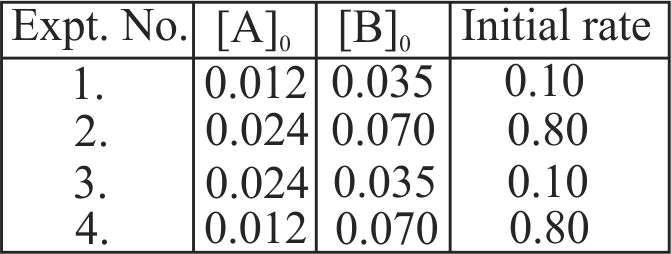
\(\mathrm{A}+2 \mathrm{~B} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}\), the rate equation for this reaction is given as, Rate \(=\mathrm{k}[\mathrm{A}][\mathrm{B}]\).
If the concentration of \(\mathrm{A}\) is kept the same but that of \(\mathrm{B}\) is doubled what will happen to the rate itself?
320185 For the reaction, \({\rm{2\;}}{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{(g)}} \to {\rm{4N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g) + }}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g)}}\) rate of reaction and rate constant are \({\rm{1}}{\rm{.2 \times 1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{ - 4}}}}\) and \({\rm{4 \times 1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{ - 5}}}}{\rm{se}}{{\rm{c}}^{{\rm{ - 1}}}}\) respectively. The concentration of \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}\) at that time will be:
320184
\(\mathrm{A}+2 \mathrm{~B} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}\), the rate equation for this reaction is given as, Rate \(=\mathrm{k}[\mathrm{A}][\mathrm{B}]\).
If the concentration of \(\mathrm{A}\) is kept the same but that of \(\mathrm{B}\) is doubled what will happen to the rate itself?
320185 For the reaction, \({\rm{2\;}}{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{(g)}} \to {\rm{4N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g) + }}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g)}}\) rate of reaction and rate constant are \({\rm{1}}{\rm{.2 \times 1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{ - 4}}}}\) and \({\rm{4 \times 1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{ - 5}}}}{\rm{se}}{{\rm{c}}^{{\rm{ - 1}}}}\) respectively. The concentration of \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}\) at that time will be:
320184
\(\mathrm{A}+2 \mathrm{~B} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}\), the rate equation for this reaction is given as, Rate \(=\mathrm{k}[\mathrm{A}][\mathrm{B}]\).
If the concentration of \(\mathrm{A}\) is kept the same but that of \(\mathrm{B}\) is doubled what will happen to the rate itself?
320185 For the reaction, \({\rm{2\;}}{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{(g)}} \to {\rm{4N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g) + }}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g)}}\) rate of reaction and rate constant are \({\rm{1}}{\rm{.2 \times 1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{ - 4}}}}\) and \({\rm{4 \times 1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{ - 5}}}}{\rm{se}}{{\rm{c}}^{{\rm{ - 1}}}}\) respectively. The concentration of \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}\) at that time will be:
320184
\(\mathrm{A}+2 \mathrm{~B} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}\), the rate equation for this reaction is given as, Rate \(=\mathrm{k}[\mathrm{A}][\mathrm{B}]\).
If the concentration of \(\mathrm{A}\) is kept the same but that of \(\mathrm{B}\) is doubled what will happen to the rate itself?
320185 For the reaction, \({\rm{2\;}}{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{(g)}} \to {\rm{4N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g) + }}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g)}}\) rate of reaction and rate constant are \({\rm{1}}{\rm{.2 \times 1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{ - 4}}}}\) and \({\rm{4 \times 1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{ - 5}}}}{\rm{se}}{{\rm{c}}^{{\rm{ - 1}}}}\) respectively. The concentration of \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}\) at that time will be:
320184
\(\mathrm{A}+2 \mathrm{~B} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}\), the rate equation for this reaction is given as, Rate \(=\mathrm{k}[\mathrm{A}][\mathrm{B}]\).
If the concentration of \(\mathrm{A}\) is kept the same but that of \(\mathrm{B}\) is doubled what will happen to the rate itself?
320185 For the reaction, \({\rm{2\;}}{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{(g)}} \to {\rm{4N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g) + }}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{(g)}}\) rate of reaction and rate constant are \({\rm{1}}{\rm{.2 \times 1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{ - 4}}}}\) and \({\rm{4 \times 1}}{{\rm{0}}^{{\rm{ - 5}}}}{\rm{se}}{{\rm{c}}^{{\rm{ - 1}}}}\) respectively. The concentration of \({{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}\) at that time will be: