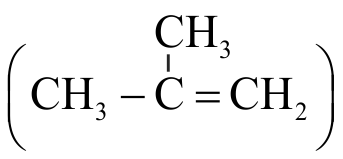318339
\(\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}\) and C in the following reactions would be
\(\mathrm{Mg}_{2} \mathrm{C}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{A}\)
\(\mathrm{Al}_{4} \mathrm{C}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{B}\)
\(\mathrm{CaC}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}\)
318339
\(\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}\) and C in the following reactions would be
\(\mathrm{Mg}_{2} \mathrm{C}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{A}\)
\(\mathrm{Al}_{4} \mathrm{C}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{B}\)
\(\mathrm{CaC}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}\)
318339
\(\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}\) and C in the following reactions would be
\(\mathrm{Mg}_{2} \mathrm{C}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{A}\)
\(\mathrm{Al}_{4} \mathrm{C}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{B}\)
\(\mathrm{CaC}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}\)
318339
\(\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}\) and C in the following reactions would be
\(\mathrm{Mg}_{2} \mathrm{C}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{A}\)
\(\mathrm{Al}_{4} \mathrm{C}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{B}\)
\(\mathrm{CaC}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}\)
318339
\(\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}\) and C in the following reactions would be
\(\mathrm{Mg}_{2} \mathrm{C}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{A}\)
\(\mathrm{Al}_{4} \mathrm{C}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{B}\)
\(\mathrm{CaC}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}\)