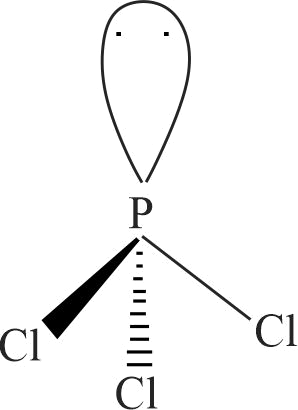
316865 On reaction with \(\mathrm{Cl}_{2}\), phosphorus forms two types of halides '\({\rm{A}}\)' and '\({\rm{B}}\)'. Halide \({\rm{A}}\) is yellowish-white powder but halide ' \(B\) ' is colourless oily liquid. Compounds " \(\mathrm{A}\) ", " \(\mathrm{B}\) " and their hydrolysis products are, respectively
316865 On reaction with \(\mathrm{Cl}_{2}\), phosphorus forms two types of halides '\({\rm{A}}\)' and '\({\rm{B}}\)'. Halide \({\rm{A}}\) is yellowish-white powder but halide ' \(B\) ' is colourless oily liquid. Compounds " \(\mathrm{A}\) ", " \(\mathrm{B}\) " and their hydrolysis products are, respectively
316865 On reaction with \(\mathrm{Cl}_{2}\), phosphorus forms two types of halides '\({\rm{A}}\)' and '\({\rm{B}}\)'. Halide \({\rm{A}}\) is yellowish-white powder but halide ' \(B\) ' is colourless oily liquid. Compounds " \(\mathrm{A}\) ", " \(\mathrm{B}\) " and their hydrolysis products are, respectively
316865 On reaction with \(\mathrm{Cl}_{2}\), phosphorus forms two types of halides '\({\rm{A}}\)' and '\({\rm{B}}\)'. Halide \({\rm{A}}\) is yellowish-white powder but halide ' \(B\) ' is colourless oily liquid. Compounds " \(\mathrm{A}\) ", " \(\mathrm{B}\) " and their hydrolysis products are, respectively