369480
Given that \(\mathrm{\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{2} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}^{\mathrm{o}}=-\mathrm{xkJ}}\) \(\mathrm{2 \mathrm{CO}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{CO}_{2} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}^{\mathrm{o}}=-\mathrm{ykJ}}\)
the enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide will be
369482
The following two reaction are known
\({\rm{F}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + 3CO}}({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{2Fe}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + 3C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}({\rm{g}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H = - 26}}.{\rm{8}}\;{\rm{kJ}}\)
\({\rm{FeO}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + CO}}({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{Fe}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}({\rm{g}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H = - 16}}.{\rm{5}}\;{\rm{kJ}}\)
The value of \(\mathrm{\Delta H}\) for the following reaction \(\mathrm{\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}(s)+\mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g}) \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeO}(s)+\mathrm{CO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})}\) is
369483
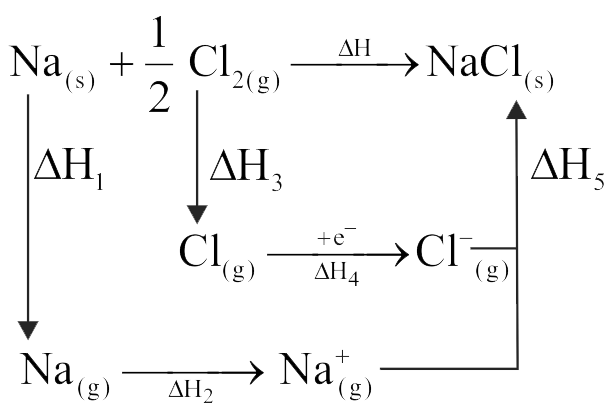
Use the following data to calculate x and y in \(\mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
(1) \(\mathrm{Na}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}^{\oplus}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=119.5\) \(\mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
(2) \(\frac{1}{2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}(\;{\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{Cl}}({\rm{g}});\Delta {\rm{H}} = {\rm{x}}\,\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
(3) \({\text{Na}}({\text{s}}) \to {\text{Na}}({\text{g}});\Delta {\text{H}} = {\text{y}}\,\,{\text{kcal}}/{\text{mol}}\)
(4) \(\mathrm{Cl}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Cl}^{-}(\mathrm{g}) ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=-87.3 \mathrm{kcal} /\) mol
\((5)\,\,{\rm{Na}}({\rm{s}}) + \frac{1}{2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}(\;{\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{NaCl}}({\rm{s}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H}} = - 98.3\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
\((6)\,\,{\rm{N}}{{\rm{a}}^ \oplus }({\rm{g}}) + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}^ - }({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{NaCl}}({\rm{s}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H}} = - 185.3\,\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
(7) \(({\rm{x}} - {\rm{y}}) = 3\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
369480
Given that \(\mathrm{\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{2} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}^{\mathrm{o}}=-\mathrm{xkJ}}\) \(\mathrm{2 \mathrm{CO}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{CO}_{2} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}^{\mathrm{o}}=-\mathrm{ykJ}}\)
the enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide will be
369482
The following two reaction are known
\({\rm{F}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + 3CO}}({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{2Fe}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + 3C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}({\rm{g}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H = - 26}}.{\rm{8}}\;{\rm{kJ}}\)
\({\rm{FeO}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + CO}}({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{Fe}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}({\rm{g}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H = - 16}}.{\rm{5}}\;{\rm{kJ}}\)
The value of \(\mathrm{\Delta H}\) for the following reaction \(\mathrm{\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}(s)+\mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g}) \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeO}(s)+\mathrm{CO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})}\) is
369483
Use the following data to calculate x and y in \(\mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
(1) \(\mathrm{Na}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}^{\oplus}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=119.5\) \(\mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
(2) \(\frac{1}{2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}(\;{\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{Cl}}({\rm{g}});\Delta {\rm{H}} = {\rm{x}}\,\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
(3) \({\text{Na}}({\text{s}}) \to {\text{Na}}({\text{g}});\Delta {\text{H}} = {\text{y}}\,\,{\text{kcal}}/{\text{mol}}\)
(4) \(\mathrm{Cl}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Cl}^{-}(\mathrm{g}) ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=-87.3 \mathrm{kcal} /\) mol
\((5)\,\,{\rm{Na}}({\rm{s}}) + \frac{1}{2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}(\;{\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{NaCl}}({\rm{s}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H}} = - 98.3\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
\((6)\,\,{\rm{N}}{{\rm{a}}^ \oplus }({\rm{g}}) + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}^ - }({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{NaCl}}({\rm{s}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H}} = - 185.3\,\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
(7) \(({\rm{x}} - {\rm{y}}) = 3\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
369480
Given that \(\mathrm{\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{2} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}^{\mathrm{o}}=-\mathrm{xkJ}}\) \(\mathrm{2 \mathrm{CO}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{CO}_{2} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}^{\mathrm{o}}=-\mathrm{ykJ}}\)
the enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide will be
369482
The following two reaction are known
\({\rm{F}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + 3CO}}({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{2Fe}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + 3C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}({\rm{g}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H = - 26}}.{\rm{8}}\;{\rm{kJ}}\)
\({\rm{FeO}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + CO}}({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{Fe}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}({\rm{g}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H = - 16}}.{\rm{5}}\;{\rm{kJ}}\)
The value of \(\mathrm{\Delta H}\) for the following reaction \(\mathrm{\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}(s)+\mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g}) \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeO}(s)+\mathrm{CO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})}\) is
369483
Use the following data to calculate x and y in \(\mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
(1) \(\mathrm{Na}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}^{\oplus}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=119.5\) \(\mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
(2) \(\frac{1}{2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}(\;{\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{Cl}}({\rm{g}});\Delta {\rm{H}} = {\rm{x}}\,\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
(3) \({\text{Na}}({\text{s}}) \to {\text{Na}}({\text{g}});\Delta {\text{H}} = {\text{y}}\,\,{\text{kcal}}/{\text{mol}}\)
(4) \(\mathrm{Cl}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Cl}^{-}(\mathrm{g}) ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=-87.3 \mathrm{kcal} /\) mol
\((5)\,\,{\rm{Na}}({\rm{s}}) + \frac{1}{2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}(\;{\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{NaCl}}({\rm{s}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H}} = - 98.3\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
\((6)\,\,{\rm{N}}{{\rm{a}}^ \oplus }({\rm{g}}) + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}^ - }({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{NaCl}}({\rm{s}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H}} = - 185.3\,\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
(7) \(({\rm{x}} - {\rm{y}}) = 3\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
369480
Given that \(\mathrm{\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{2} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}^{\mathrm{o}}=-\mathrm{xkJ}}\) \(\mathrm{2 \mathrm{CO}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{CO}_{2} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}^{\mathrm{o}}=-\mathrm{ykJ}}\)
the enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide will be
369482
The following two reaction are known
\({\rm{F}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + 3CO}}({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{2Fe}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + 3C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}({\rm{g}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H = - 26}}.{\rm{8}}\;{\rm{kJ}}\)
\({\rm{FeO}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + CO}}({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{Fe}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}({\rm{g}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H = - 16}}.{\rm{5}}\;{\rm{kJ}}\)
The value of \(\mathrm{\Delta H}\) for the following reaction \(\mathrm{\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}(s)+\mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g}) \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeO}(s)+\mathrm{CO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})}\) is
369483
Use the following data to calculate x and y in \(\mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
(1) \(\mathrm{Na}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}^{\oplus}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=119.5\) \(\mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
(2) \(\frac{1}{2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}(\;{\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{Cl}}({\rm{g}});\Delta {\rm{H}} = {\rm{x}}\,\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
(3) \({\text{Na}}({\text{s}}) \to {\text{Na}}({\text{g}});\Delta {\text{H}} = {\text{y}}\,\,{\text{kcal}}/{\text{mol}}\)
(4) \(\mathrm{Cl}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Cl}^{-}(\mathrm{g}) ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=-87.3 \mathrm{kcal} /\) mol
\((5)\,\,{\rm{Na}}({\rm{s}}) + \frac{1}{2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}(\;{\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{NaCl}}({\rm{s}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H}} = - 98.3\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
\((6)\,\,{\rm{N}}{{\rm{a}}^ \oplus }({\rm{g}}) + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}^ - }({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{NaCl}}({\rm{s}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H}} = - 185.3\,\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
(7) \(({\rm{x}} - {\rm{y}}) = 3\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
369480
Given that \(\mathrm{\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{2} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}^{\mathrm{o}}=-\mathrm{xkJ}}\) \(\mathrm{2 \mathrm{CO}+\mathrm{O}_{2} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{CO}_{2} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}^{\mathrm{o}}=-\mathrm{ykJ}}\)
the enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide will be
369482
The following two reaction are known
\({\rm{F}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + 3CO}}({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{2Fe}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + 3C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}({\rm{g}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H = - 26}}.{\rm{8}}\;{\rm{kJ}}\)
\({\rm{FeO}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + CO}}({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{Fe}}({\rm{s}}){\rm{ + C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}({\rm{g}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H = - 16}}.{\rm{5}}\;{\rm{kJ}}\)
The value of \(\mathrm{\Delta H}\) for the following reaction \(\mathrm{\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}(s)+\mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g}) \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeO}(s)+\mathrm{CO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})}\) is
369483
Use the following data to calculate x and y in \(\mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
(1) \(\mathrm{Na}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}^{\oplus}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-} ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=119.5\) \(\mathrm{kcal} / \mathrm{mol}\)
(2) \(\frac{1}{2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}(\;{\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{Cl}}({\rm{g}});\Delta {\rm{H}} = {\rm{x}}\,\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
(3) \({\text{Na}}({\text{s}}) \to {\text{Na}}({\text{g}});\Delta {\text{H}} = {\text{y}}\,\,{\text{kcal}}/{\text{mol}}\)
(4) \(\mathrm{Cl}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Cl}^{-}(\mathrm{g}) ; \Delta \mathrm{H}=-87.3 \mathrm{kcal} /\) mol
\((5)\,\,{\rm{Na}}({\rm{s}}) + \frac{1}{2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}(\;{\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{NaCl}}({\rm{s}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H}} = - 98.3\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
\((6)\,\,{\rm{N}}{{\rm{a}}^ \oplus }({\rm{g}}) + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}^ - }({\rm{g}}) \to {\rm{NaCl}}({\rm{s}});\)
\(\Delta {\rm{H}} = - 185.3\,\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)
(7) \(({\rm{x}} - {\rm{y}}) = 3\,{\rm{kcal}}/{\rm{mol}}\)