358136
Assertion :
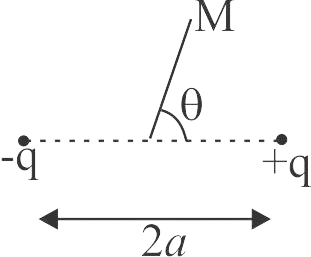
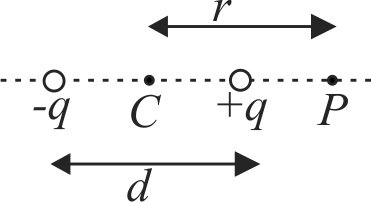
The electric field due to a dipole on its axial line at a distance \(r\) is \(E\). Then, electric field due to the same dipole on the equatorial line and at the same distance will be \(\dfrac{E}{2}\)
Reason :
Electric field due to dipole varies inversely as the square of distance on axial line.
358136
Assertion :
The electric field due to a dipole on its axial line at a distance \(r\) is \(E\). Then, electric field due to the same dipole on the equatorial line and at the same distance will be \(\dfrac{E}{2}\)
Reason :
Electric field due to dipole varies inversely as the square of distance on axial line.
358136
Assertion :
The electric field due to a dipole on its axial line at a distance \(r\) is \(E\). Then, electric field due to the same dipole on the equatorial line and at the same distance will be \(\dfrac{E}{2}\)
Reason :
Electric field due to dipole varies inversely as the square of distance on axial line.
358136
Assertion :
The electric field due to a dipole on its axial line at a distance \(r\) is \(E\). Then, electric field due to the same dipole on the equatorial line and at the same distance will be \(\dfrac{E}{2}\)
Reason :
Electric field due to dipole varies inversely as the square of distance on axial line.
358136
Assertion :
The electric field due to a dipole on its axial line at a distance \(r\) is \(E\). Then, electric field due to the same dipole on the equatorial line and at the same distance will be \(\dfrac{E}{2}\)
Reason :
Electric field due to dipole varies inversely as the square of distance on axial line.