357961
Point charge \({q=5 {C}}\) is placed at a point on the axis of a square non-conducting surface. The axis is perpendicular to the square surface and is passing through its centre. Flux of electric field through the square caused due to charge \({q}\) is \({\phi=75 {~N}-{m}^{2} / {C}}\). If the square is given a surface charge of uniform density \({\sigma=20\,\, {C} / {m}^{2}}\), find the force on the square surface due to point charge \({q}\).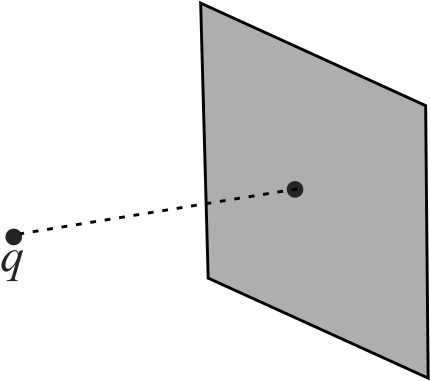
357961
Point charge \({q=5 {C}}\) is placed at a point on the axis of a square non-conducting surface. The axis is perpendicular to the square surface and is passing through its centre. Flux of electric field through the square caused due to charge \({q}\) is \({\phi=75 {~N}-{m}^{2} / {C}}\). If the square is given a surface charge of uniform density \({\sigma=20\,\, {C} / {m}^{2}}\), find the force on the square surface due to point charge \({q}\).
357961
Point charge \({q=5 {C}}\) is placed at a point on the axis of a square non-conducting surface. The axis is perpendicular to the square surface and is passing through its centre. Flux of electric field through the square caused due to charge \({q}\) is \({\phi=75 {~N}-{m}^{2} / {C}}\). If the square is given a surface charge of uniform density \({\sigma=20\,\, {C} / {m}^{2}}\), find the force on the square surface due to point charge \({q}\).
357961
Point charge \({q=5 {C}}\) is placed at a point on the axis of a square non-conducting surface. The axis is perpendicular to the square surface and is passing through its centre. Flux of electric field through the square caused due to charge \({q}\) is \({\phi=75 {~N}-{m}^{2} / {C}}\). If the square is given a surface charge of uniform density \({\sigma=20\,\, {C} / {m}^{2}}\), find the force on the square surface due to point charge \({q}\).