357740
In the figure shown electromagnetic radiations of wavelength \(200\,nm\) are incident on the metallic plate \({A}\). The photo electrons are accelerated by a potential difference \(10\,V\). These electrons strike another metal plate \({B}\) from which electromagnetic radiations are emitted. The minimum wavelength of the emitted photons is \(100\,nm\). If the work function of the metal ' \({A}\) ' is found to be \(1.9\,NeV\). The value of \({N}\) is ____ .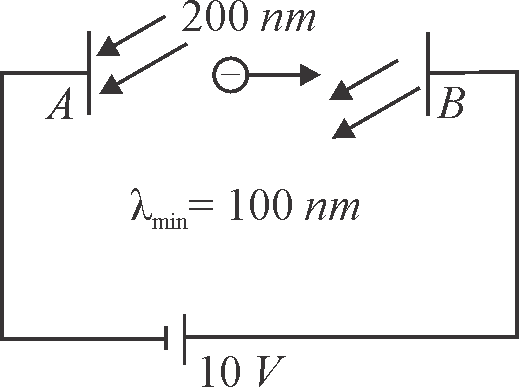
Use \(hv = 12400\,eV\) \( \mathop A^{~~\circ} \), use \(Rch = 13.6\,eV.\)
357742
Work-function for caesium metal is \(2.14\,eV.\) Let a beam of light of frequency \(6 \times {10^{14}}\;Hz\) is incident over the metal surface. Now, match the following columns and choose the correct option
Column I
Column II
A
maximum \(KE\) of emitted photoelectrons (in \(eV\))
P
334 \(km{s^{ - 1}}\)
B
Minimum \(KE\) of emitted photoelectrons (in \(eV\)
Q
345 \(mV\)
C
Stopping potential of material ( in \(mV\)) is
R
\(0.345\,eV\)
D
Maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons ( in \(km{s^{ - 1}}\))
S
0
357740
In the figure shown electromagnetic radiations of wavelength \(200\,nm\) are incident on the metallic plate \({A}\). The photo electrons are accelerated by a potential difference \(10\,V\). These electrons strike another metal plate \({B}\) from which electromagnetic radiations are emitted. The minimum wavelength of the emitted photons is \(100\,nm\). If the work function of the metal ' \({A}\) ' is found to be \(1.9\,NeV\). The value of \({N}\) is ____ .
Use \(hv = 12400\,eV\) \( \mathop A^{~~\circ} \), use \(Rch = 13.6\,eV.\)
357742
Work-function for caesium metal is \(2.14\,eV.\) Let a beam of light of frequency \(6 \times {10^{14}}\;Hz\) is incident over the metal surface. Now, match the following columns and choose the correct option
Column I
Column II
A
maximum \(KE\) of emitted photoelectrons (in \(eV\))
P
334 \(km{s^{ - 1}}\)
B
Minimum \(KE\) of emitted photoelectrons (in \(eV\)
Q
345 \(mV\)
C
Stopping potential of material ( in \(mV\)) is
R
\(0.345\,eV\)
D
Maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons ( in \(km{s^{ - 1}}\))
S
0
357740
In the figure shown electromagnetic radiations of wavelength \(200\,nm\) are incident on the metallic plate \({A}\). The photo electrons are accelerated by a potential difference \(10\,V\). These electrons strike another metal plate \({B}\) from which electromagnetic radiations are emitted. The minimum wavelength of the emitted photons is \(100\,nm\). If the work function of the metal ' \({A}\) ' is found to be \(1.9\,NeV\). The value of \({N}\) is ____ .
Use \(hv = 12400\,eV\) \( \mathop A^{~~\circ} \), use \(Rch = 13.6\,eV.\)
357742
Work-function for caesium metal is \(2.14\,eV.\) Let a beam of light of frequency \(6 \times {10^{14}}\;Hz\) is incident over the metal surface. Now, match the following columns and choose the correct option
Column I
Column II
A
maximum \(KE\) of emitted photoelectrons (in \(eV\))
P
334 \(km{s^{ - 1}}\)
B
Minimum \(KE\) of emitted photoelectrons (in \(eV\)
Q
345 \(mV\)
C
Stopping potential of material ( in \(mV\)) is
R
\(0.345\,eV\)
D
Maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons ( in \(km{s^{ - 1}}\))
S
0
357740
In the figure shown electromagnetic radiations of wavelength \(200\,nm\) are incident on the metallic plate \({A}\). The photo electrons are accelerated by a potential difference \(10\,V\). These electrons strike another metal plate \({B}\) from which electromagnetic radiations are emitted. The minimum wavelength of the emitted photons is \(100\,nm\). If the work function of the metal ' \({A}\) ' is found to be \(1.9\,NeV\). The value of \({N}\) is ____ .
Use \(hv = 12400\,eV\) \( \mathop A^{~~\circ} \), use \(Rch = 13.6\,eV.\)
357742
Work-function for caesium metal is \(2.14\,eV.\) Let a beam of light of frequency \(6 \times {10^{14}}\;Hz\) is incident over the metal surface. Now, match the following columns and choose the correct option
Column I
Column II
A
maximum \(KE\) of emitted photoelectrons (in \(eV\))
P
334 \(km{s^{ - 1}}\)
B
Minimum \(KE\) of emitted photoelectrons (in \(eV\)
Q
345 \(mV\)
C
Stopping potential of material ( in \(mV\)) is
R
\(0.345\,eV\)
D
Maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons ( in \(km{s^{ - 1}}\))
S
0
357740
In the figure shown electromagnetic radiations of wavelength \(200\,nm\) are incident on the metallic plate \({A}\). The photo electrons are accelerated by a potential difference \(10\,V\). These electrons strike another metal plate \({B}\) from which electromagnetic radiations are emitted. The minimum wavelength of the emitted photons is \(100\,nm\). If the work function of the metal ' \({A}\) ' is found to be \(1.9\,NeV\). The value of \({N}\) is ____ .
Use \(hv = 12400\,eV\) \( \mathop A^{~~\circ} \), use \(Rch = 13.6\,eV.\)
357742
Work-function for caesium metal is \(2.14\,eV.\) Let a beam of light of frequency \(6 \times {10^{14}}\;Hz\) is incident over the metal surface. Now, match the following columns and choose the correct option
Column I
Column II
A
maximum \(KE\) of emitted photoelectrons (in \(eV\))
P
334 \(km{s^{ - 1}}\)
B
Minimum \(KE\) of emitted photoelectrons (in \(eV\)
Q
345 \(mV\)
C
Stopping potential of material ( in \(mV\)) is
R
\(0.345\,eV\)
D
Maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons ( in \(km{s^{ - 1}}\))
S
0