356305
In the circuit shown the transformer is ideal with turn ratio \({\dfrac{N_{1}}{N_{2}}=\dfrac{5}{1}}\). The voltage of the source is \({V_{{s}}=300 {~V}}\).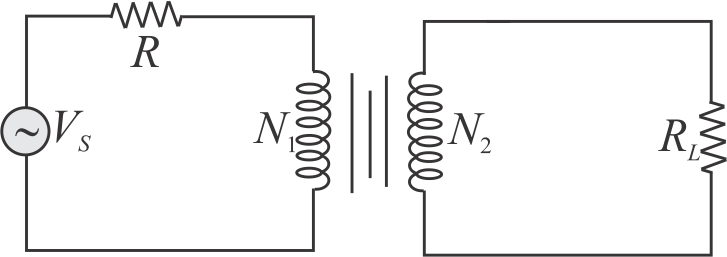
The voltage measured across the load resistance \({R_{l}}\) is 50 \(V\) . Find the value of resistance \({R(}\) in \({\Omega}\) ) in the primary circuit.
356305
In the circuit shown the transformer is ideal with turn ratio \({\dfrac{N_{1}}{N_{2}}=\dfrac{5}{1}}\). The voltage of the source is \({V_{{s}}=300 {~V}}\).
The voltage measured across the load resistance \({R_{l}}\) is 50 \(V\) . Find the value of resistance \({R(}\) in \({\Omega}\) ) in the primary circuit.
356305
In the circuit shown the transformer is ideal with turn ratio \({\dfrac{N_{1}}{N_{2}}=\dfrac{5}{1}}\). The voltage of the source is \({V_{{s}}=300 {~V}}\).
The voltage measured across the load resistance \({R_{l}}\) is 50 \(V\) . Find the value of resistance \({R(}\) in \({\Omega}\) ) in the primary circuit.
356305
In the circuit shown the transformer is ideal with turn ratio \({\dfrac{N_{1}}{N_{2}}=\dfrac{5}{1}}\). The voltage of the source is \({V_{{s}}=300 {~V}}\).
The voltage measured across the load resistance \({R_{l}}\) is 50 \(V\) . Find the value of resistance \({R(}\) in \({\Omega}\) ) in the primary circuit.