C: There is different image formed by concave mirror. It mainly depends on the distance between the object and the mirror.
Concave mirror form both real and virtual images. When concave mirror is placed very close to the object, a virtual and magnified image is obtained and if we increase the distance between the object and mirror, the size of the image reduces and real image are formula.
Hence, image formed by a concave mirror is certainly real if the object is virtual.
UPSEE - 2008
Ray Optics
281991
What is the minimum size of mirror required for a $6 \mathrm{ft}$ tall person to be able to see a full length image?
1 $6 \mathrm{ft}$
2 $4.5 \mathrm{ft}$
3 $3 \mathrm{ft}$
4 $1 \mathrm{ft}$
Explanation:
C: For seeing full length image in plane mirror. The size of plane mirror should be half of the object.
Hence, size of mirror $=\frac{6}{2}=3 \mathrm{ft}$
SRMJEEE - 2016
Ray Optics
281992
To get three images of a single object, we should have two plane mirrors at an angle of
1 $60^{\circ}$
2 $90^{\circ}$
3 $120^{\circ}$
4 $30^{\circ}$
Explanation:
B: Given, number of images (n) $=3$
Number of images $(n)=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1$
$\begin{aligned}
3=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1 \\
4=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta} \\
\theta=90^{\circ}
\end{aligned}$
JIPMER-2014
Ray Optics
281993
A object moving at a speed of $5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ towards concave mirror of focal length $f=1 \mathrm{~m}$ is at distance of $9 \mathrm{~m}$. The average speed of the image is
1 $\frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
2 $\frac{1}{10} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
3 $\frac{5}{9} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
4 $\frac{4}{10} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
Explanation:
A:
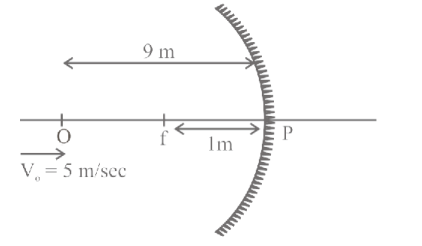
Given, focal length $(\mathrm{f})=-1 \mathrm{~m}$
Object distance $(\mathrm{u})=-9 \mathrm{~m}$
Object velocity $\left(\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}\right)=5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$
From mirror formula
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
-\frac{1}{1}=-\frac{1}{9}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{9}-1 \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=-\frac{8}{9} \mathrm{~m} \\
\mathrm{v}=-\frac{9}{8} \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}$
In 1 second, object travel $\Delta \mathrm{u}=5 \mathrm{~m}$ Then $\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{f}}=(-9+5)=-4 \mathrm{~m}$ (toward pole) Now,
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{f}}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{~V}_{\mathrm{f}}} \\
-1=-\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{f}}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{f}}}=\frac{1}{4}-1
\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{v_f}=\frac{-3}{4} \\
v_f=-\frac{4}{3} m
\end{aligned}$
Change in image position
$\Delta \mathrm{V}=-\frac{9}{8}+\frac{4}{3}=\frac{-27+32}{24}=\frac{5}{24} \square \frac{1}{4.8}$
In one second,
Average speed of image $=\frac{1}{4.8} \square \frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$
AMU-2010
Ray Optics
281994
Light rays of different colours move in air with the
1 Same velocity
2 Velocity of air
3 Different velocity
4 Velocity of sound
Explanation:
C: In vacuum, all colors of light travel with same speed (i.e. $\mathrm{c}=3 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$ ). But light of different colors travels at different speeds when they travel through air or any medium.
C: There is different image formed by concave mirror. It mainly depends on the distance between the object and the mirror.
Concave mirror form both real and virtual images. When concave mirror is placed very close to the object, a virtual and magnified image is obtained and if we increase the distance between the object and mirror, the size of the image reduces and real image are formula.
Hence, image formed by a concave mirror is certainly real if the object is virtual.
UPSEE - 2008
Ray Optics
281991
What is the minimum size of mirror required for a $6 \mathrm{ft}$ tall person to be able to see a full length image?
1 $6 \mathrm{ft}$
2 $4.5 \mathrm{ft}$
3 $3 \mathrm{ft}$
4 $1 \mathrm{ft}$
Explanation:
C: For seeing full length image in plane mirror. The size of plane mirror should be half of the object.
Hence, size of mirror $=\frac{6}{2}=3 \mathrm{ft}$
SRMJEEE - 2016
Ray Optics
281992
To get three images of a single object, we should have two plane mirrors at an angle of
1 $60^{\circ}$
2 $90^{\circ}$
3 $120^{\circ}$
4 $30^{\circ}$
Explanation:
B: Given, number of images (n) $=3$
Number of images $(n)=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1$
$\begin{aligned}
3=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1 \\
4=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta} \\
\theta=90^{\circ}
\end{aligned}$
JIPMER-2014
Ray Optics
281993
A object moving at a speed of $5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ towards concave mirror of focal length $f=1 \mathrm{~m}$ is at distance of $9 \mathrm{~m}$. The average speed of the image is
1 $\frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
2 $\frac{1}{10} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
3 $\frac{5}{9} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
4 $\frac{4}{10} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
Explanation:
A:

Given, focal length $(\mathrm{f})=-1 \mathrm{~m}$
Object distance $(\mathrm{u})=-9 \mathrm{~m}$
Object velocity $\left(\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}\right)=5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$
From mirror formula
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
-\frac{1}{1}=-\frac{1}{9}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{9}-1 \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=-\frac{8}{9} \mathrm{~m} \\
\mathrm{v}=-\frac{9}{8} \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}$
In 1 second, object travel $\Delta \mathrm{u}=5 \mathrm{~m}$ Then $\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{f}}=(-9+5)=-4 \mathrm{~m}$ (toward pole) Now,
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{f}}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{~V}_{\mathrm{f}}} \\
-1=-\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{f}}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{f}}}=\frac{1}{4}-1
\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{v_f}=\frac{-3}{4} \\
v_f=-\frac{4}{3} m
\end{aligned}$
Change in image position
$\Delta \mathrm{V}=-\frac{9}{8}+\frac{4}{3}=\frac{-27+32}{24}=\frac{5}{24} \square \frac{1}{4.8}$
In one second,
Average speed of image $=\frac{1}{4.8} \square \frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$
AMU-2010
Ray Optics
281994
Light rays of different colours move in air with the
1 Same velocity
2 Velocity of air
3 Different velocity
4 Velocity of sound
Explanation:
C: In vacuum, all colors of light travel with same speed (i.e. $\mathrm{c}=3 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$ ). But light of different colors travels at different speeds when they travel through air or any medium.
NEET Test Series from KOTA - 10 Papers In MS WORD
WhatsApp Here
Ray Optics
281957
The image formed by a concave mirror
1 is always real
2 is always virtual
3 is certainly real if the object is virtual
4 is certainly virtual
Explanation:
C: There is different image formed by concave mirror. It mainly depends on the distance between the object and the mirror.
Concave mirror form both real and virtual images. When concave mirror is placed very close to the object, a virtual and magnified image is obtained and if we increase the distance between the object and mirror, the size of the image reduces and real image are formula.
Hence, image formed by a concave mirror is certainly real if the object is virtual.
UPSEE - 2008
Ray Optics
281991
What is the minimum size of mirror required for a $6 \mathrm{ft}$ tall person to be able to see a full length image?
1 $6 \mathrm{ft}$
2 $4.5 \mathrm{ft}$
3 $3 \mathrm{ft}$
4 $1 \mathrm{ft}$
Explanation:
C: For seeing full length image in plane mirror. The size of plane mirror should be half of the object.
Hence, size of mirror $=\frac{6}{2}=3 \mathrm{ft}$
SRMJEEE - 2016
Ray Optics
281992
To get three images of a single object, we should have two plane mirrors at an angle of
1 $60^{\circ}$
2 $90^{\circ}$
3 $120^{\circ}$
4 $30^{\circ}$
Explanation:
B: Given, number of images (n) $=3$
Number of images $(n)=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1$
$\begin{aligned}
3=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1 \\
4=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta} \\
\theta=90^{\circ}
\end{aligned}$
JIPMER-2014
Ray Optics
281993
A object moving at a speed of $5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ towards concave mirror of focal length $f=1 \mathrm{~m}$ is at distance of $9 \mathrm{~m}$. The average speed of the image is
1 $\frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
2 $\frac{1}{10} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
3 $\frac{5}{9} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
4 $\frac{4}{10} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
Explanation:
A:

Given, focal length $(\mathrm{f})=-1 \mathrm{~m}$
Object distance $(\mathrm{u})=-9 \mathrm{~m}$
Object velocity $\left(\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}\right)=5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$
From mirror formula
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
-\frac{1}{1}=-\frac{1}{9}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{9}-1 \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=-\frac{8}{9} \mathrm{~m} \\
\mathrm{v}=-\frac{9}{8} \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}$
In 1 second, object travel $\Delta \mathrm{u}=5 \mathrm{~m}$ Then $\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{f}}=(-9+5)=-4 \mathrm{~m}$ (toward pole) Now,
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{f}}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{~V}_{\mathrm{f}}} \\
-1=-\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{f}}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{f}}}=\frac{1}{4}-1
\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{v_f}=\frac{-3}{4} \\
v_f=-\frac{4}{3} m
\end{aligned}$
Change in image position
$\Delta \mathrm{V}=-\frac{9}{8}+\frac{4}{3}=\frac{-27+32}{24}=\frac{5}{24} \square \frac{1}{4.8}$
In one second,
Average speed of image $=\frac{1}{4.8} \square \frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$
AMU-2010
Ray Optics
281994
Light rays of different colours move in air with the
1 Same velocity
2 Velocity of air
3 Different velocity
4 Velocity of sound
Explanation:
C: In vacuum, all colors of light travel with same speed (i.e. $\mathrm{c}=3 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$ ). But light of different colors travels at different speeds when they travel through air or any medium.
C: There is different image formed by concave mirror. It mainly depends on the distance between the object and the mirror.
Concave mirror form both real and virtual images. When concave mirror is placed very close to the object, a virtual and magnified image is obtained and if we increase the distance between the object and mirror, the size of the image reduces and real image are formula.
Hence, image formed by a concave mirror is certainly real if the object is virtual.
UPSEE - 2008
Ray Optics
281991
What is the minimum size of mirror required for a $6 \mathrm{ft}$ tall person to be able to see a full length image?
1 $6 \mathrm{ft}$
2 $4.5 \mathrm{ft}$
3 $3 \mathrm{ft}$
4 $1 \mathrm{ft}$
Explanation:
C: For seeing full length image in plane mirror. The size of plane mirror should be half of the object.
Hence, size of mirror $=\frac{6}{2}=3 \mathrm{ft}$
SRMJEEE - 2016
Ray Optics
281992
To get three images of a single object, we should have two plane mirrors at an angle of
1 $60^{\circ}$
2 $90^{\circ}$
3 $120^{\circ}$
4 $30^{\circ}$
Explanation:
B: Given, number of images (n) $=3$
Number of images $(n)=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1$
$\begin{aligned}
3=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1 \\
4=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta} \\
\theta=90^{\circ}
\end{aligned}$
JIPMER-2014
Ray Optics
281993
A object moving at a speed of $5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ towards concave mirror of focal length $f=1 \mathrm{~m}$ is at distance of $9 \mathrm{~m}$. The average speed of the image is
1 $\frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
2 $\frac{1}{10} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
3 $\frac{5}{9} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
4 $\frac{4}{10} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
Explanation:
A:

Given, focal length $(\mathrm{f})=-1 \mathrm{~m}$
Object distance $(\mathrm{u})=-9 \mathrm{~m}$
Object velocity $\left(\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}\right)=5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$
From mirror formula
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
-\frac{1}{1}=-\frac{1}{9}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{9}-1 \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=-\frac{8}{9} \mathrm{~m} \\
\mathrm{v}=-\frac{9}{8} \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}$
In 1 second, object travel $\Delta \mathrm{u}=5 \mathrm{~m}$ Then $\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{f}}=(-9+5)=-4 \mathrm{~m}$ (toward pole) Now,
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{f}}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{~V}_{\mathrm{f}}} \\
-1=-\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{f}}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{f}}}=\frac{1}{4}-1
\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{v_f}=\frac{-3}{4} \\
v_f=-\frac{4}{3} m
\end{aligned}$
Change in image position
$\Delta \mathrm{V}=-\frac{9}{8}+\frac{4}{3}=\frac{-27+32}{24}=\frac{5}{24} \square \frac{1}{4.8}$
In one second,
Average speed of image $=\frac{1}{4.8} \square \frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$
AMU-2010
Ray Optics
281994
Light rays of different colours move in air with the
1 Same velocity
2 Velocity of air
3 Different velocity
4 Velocity of sound
Explanation:
C: In vacuum, all colors of light travel with same speed (i.e. $\mathrm{c}=3 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$ ). But light of different colors travels at different speeds when they travel through air or any medium.
C: There is different image formed by concave mirror. It mainly depends on the distance between the object and the mirror.
Concave mirror form both real and virtual images. When concave mirror is placed very close to the object, a virtual and magnified image is obtained and if we increase the distance between the object and mirror, the size of the image reduces and real image are formula.
Hence, image formed by a concave mirror is certainly real if the object is virtual.
UPSEE - 2008
Ray Optics
281991
What is the minimum size of mirror required for a $6 \mathrm{ft}$ tall person to be able to see a full length image?
1 $6 \mathrm{ft}$
2 $4.5 \mathrm{ft}$
3 $3 \mathrm{ft}$
4 $1 \mathrm{ft}$
Explanation:
C: For seeing full length image in plane mirror. The size of plane mirror should be half of the object.
Hence, size of mirror $=\frac{6}{2}=3 \mathrm{ft}$
SRMJEEE - 2016
Ray Optics
281992
To get three images of a single object, we should have two plane mirrors at an angle of
1 $60^{\circ}$
2 $90^{\circ}$
3 $120^{\circ}$
4 $30^{\circ}$
Explanation:
B: Given, number of images (n) $=3$
Number of images $(n)=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1$
$\begin{aligned}
3=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta}-1 \\
4=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\theta} \\
\theta=90^{\circ}
\end{aligned}$
JIPMER-2014
Ray Optics
281993
A object moving at a speed of $5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ towards concave mirror of focal length $f=1 \mathrm{~m}$ is at distance of $9 \mathrm{~m}$. The average speed of the image is
1 $\frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
2 $\frac{1}{10} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
3 $\frac{5}{9} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
4 $\frac{4}{10} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
Explanation:
A:

Given, focal length $(\mathrm{f})=-1 \mathrm{~m}$
Object distance $(\mathrm{u})=-9 \mathrm{~m}$
Object velocity $\left(\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}\right)=5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$
From mirror formula
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
-\frac{1}{1}=-\frac{1}{9}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=\frac{1}{9}-1 \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}=-\frac{8}{9} \mathrm{~m} \\
\mathrm{v}=-\frac{9}{8} \mathrm{~m}
\end{aligned}$
In 1 second, object travel $\Delta \mathrm{u}=5 \mathrm{~m}$ Then $\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{f}}=(-9+5)=-4 \mathrm{~m}$ (toward pole) Now,
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{f}}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{~V}_{\mathrm{f}}} \\
-1=-\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{f}}} \\
\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{f}}}=\frac{1}{4}-1
\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned}
\frac{1}{v_f}=\frac{-3}{4} \\
v_f=-\frac{4}{3} m
\end{aligned}$
Change in image position
$\Delta \mathrm{V}=-\frac{9}{8}+\frac{4}{3}=\frac{-27+32}{24}=\frac{5}{24} \square \frac{1}{4.8}$
In one second,
Average speed of image $=\frac{1}{4.8} \square \frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$
AMU-2010
Ray Optics
281994
Light rays of different colours move in air with the
1 Same velocity
2 Velocity of air
3 Different velocity
4 Velocity of sound
Explanation:
C: In vacuum, all colors of light travel with same speed (i.e. $\mathrm{c}=3 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{sec}$ ). But light of different colors travels at different speeds when they travel through air or any medium.