142428
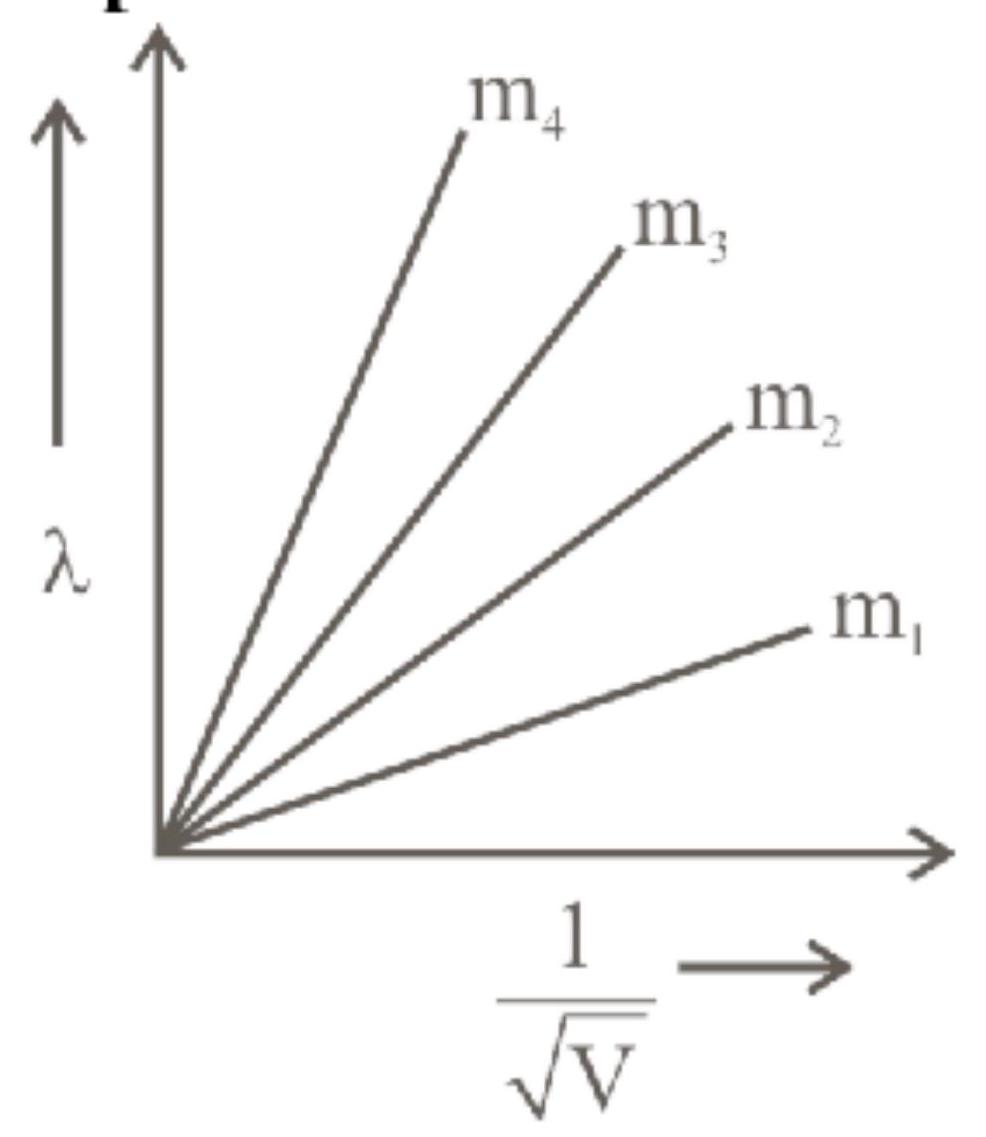
According to de-Broglie hypothesis if an electron of mass '
142428
According to de-Broglie hypothesis if an electron of mass '
142428
According to de-Broglie hypothesis if an electron of mass '
142428
According to de-Broglie hypothesis if an electron of mass '