142426
Graph shows the variation of de-Broglie wavelength $(\lambda)$ versus $\frac{1}{\sqrt{V}}$, where ' $V$ ' is the accelerating potential for four particles carrying same charge but of masses $m_{1}, m_{2}, m_{3}$, $\mathrm{m}_{4}$. Which particle has a smaller mass?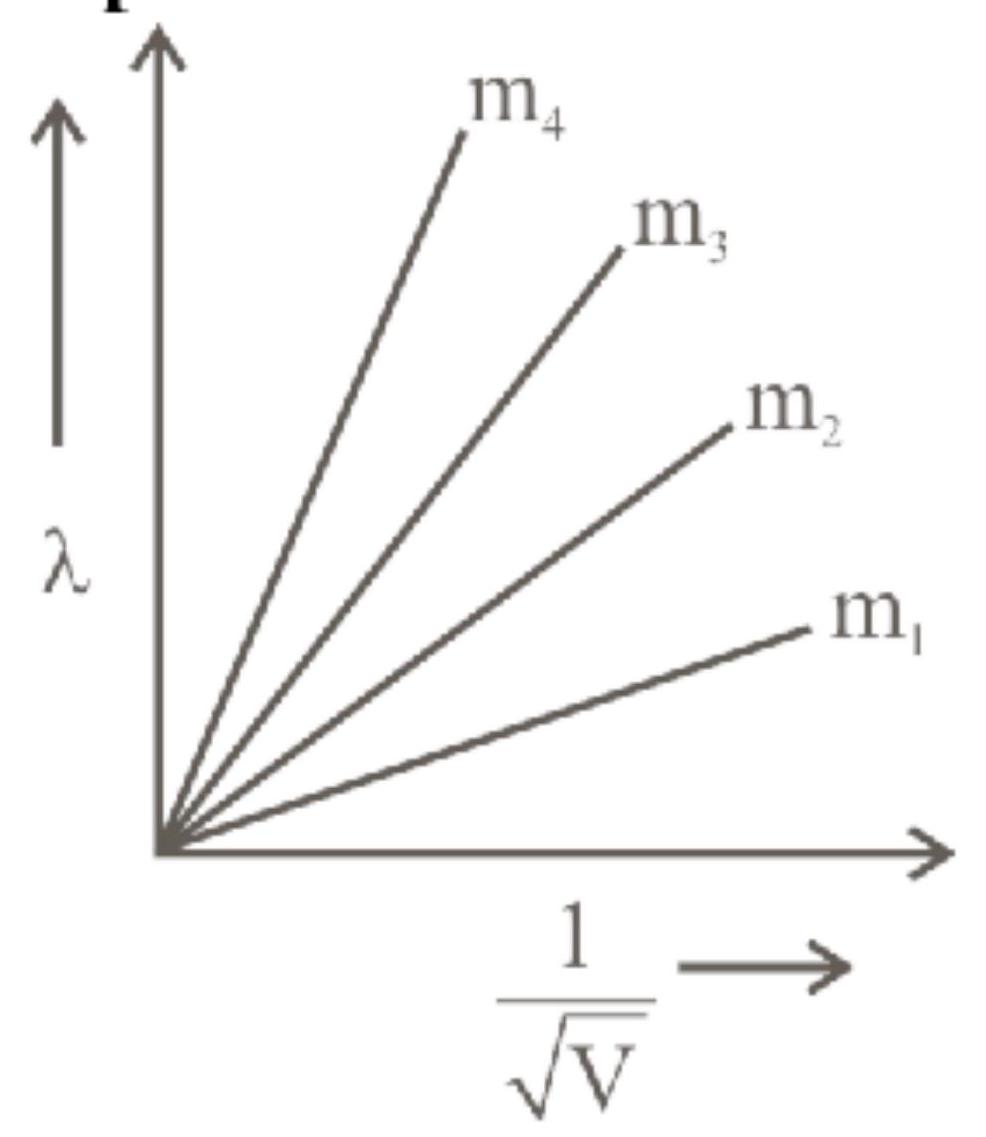
142428 According to de-Broglie hypothesis if an electron of mass ' $m$ ' is accelerated by potential difference ' $V$ ', then associated wavelength is ' $\lambda$ '. When a proton of mass ' $M$ ' is accelerated through potential difference of ' $9 \mathrm{~V}$ ', then the wavelength associated with it, is
142426
Graph shows the variation of de-Broglie wavelength $(\lambda)$ versus $\frac{1}{\sqrt{V}}$, where ' $V$ ' is the accelerating potential for four particles carrying same charge but of masses $m_{1}, m_{2}, m_{3}$, $\mathrm{m}_{4}$. Which particle has a smaller mass?
142428 According to de-Broglie hypothesis if an electron of mass ' $m$ ' is accelerated by potential difference ' $V$ ', then associated wavelength is ' $\lambda$ '. When a proton of mass ' $M$ ' is accelerated through potential difference of ' $9 \mathrm{~V}$ ', then the wavelength associated with it, is
142426
Graph shows the variation of de-Broglie wavelength $(\lambda)$ versus $\frac{1}{\sqrt{V}}$, where ' $V$ ' is the accelerating potential for four particles carrying same charge but of masses $m_{1}, m_{2}, m_{3}$, $\mathrm{m}_{4}$. Which particle has a smaller mass?
142428 According to de-Broglie hypothesis if an electron of mass ' $m$ ' is accelerated by potential difference ' $V$ ', then associated wavelength is ' $\lambda$ '. When a proton of mass ' $M$ ' is accelerated through potential difference of ' $9 \mathrm{~V}$ ', then the wavelength associated with it, is
142426
Graph shows the variation of de-Broglie wavelength $(\lambda)$ versus $\frac{1}{\sqrt{V}}$, where ' $V$ ' is the accelerating potential for four particles carrying same charge but of masses $m_{1}, m_{2}, m_{3}$, $\mathrm{m}_{4}$. Which particle has a smaller mass?
142428 According to de-Broglie hypothesis if an electron of mass ' $m$ ' is accelerated by potential difference ' $V$ ', then associated wavelength is ' $\lambda$ '. When a proton of mass ' $M$ ' is accelerated through potential difference of ' $9 \mathrm{~V}$ ', then the wavelength associated with it, is
