138478 The mass of the earth is $6.00 \times 10^{24} \mathrm{~kg}$ and that of the moon is $7.40 \times 10^{22} \mathrm{~kg}$. The constant of gravitation $G=6.67 \times 10^{-1 i} \mathrm{~N}-\mathrm{m}^{2} / \mathrm{kg}^{2}$. The potential energy of the system is $-7.79 \times 10^{28} \mathrm{~J}$. The mean distance between the earth and moon is
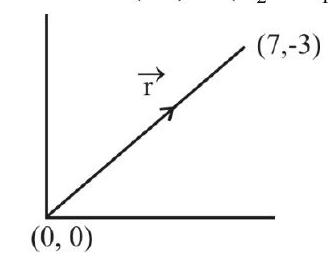
138479 The gravitational field in a region is given by $\mathrm{g}=5 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{kg} \hat{\mathrm{i}}+12 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{kg} \hat{\mathbf{j}}$. The change in the gravitational potential energy of a particle of mass $1 \mathrm{~kg}$ when it is taken from the origin to a point $(7 m,-3 m)$ is:
138478 The mass of the earth is $6.00 \times 10^{24} \mathrm{~kg}$ and that of the moon is $7.40 \times 10^{22} \mathrm{~kg}$. The constant of gravitation $G=6.67 \times 10^{-1 i} \mathrm{~N}-\mathrm{m}^{2} / \mathrm{kg}^{2}$. The potential energy of the system is $-7.79 \times 10^{28} \mathrm{~J}$. The mean distance between the earth and moon is
138479 The gravitational field in a region is given by $\mathrm{g}=5 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{kg} \hat{\mathrm{i}}+12 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{kg} \hat{\mathbf{j}}$. The change in the gravitational potential energy of a particle of mass $1 \mathrm{~kg}$ when it is taken from the origin to a point $(7 m,-3 m)$ is:
138478 The mass of the earth is $6.00 \times 10^{24} \mathrm{~kg}$ and that of the moon is $7.40 \times 10^{22} \mathrm{~kg}$. The constant of gravitation $G=6.67 \times 10^{-1 i} \mathrm{~N}-\mathrm{m}^{2} / \mathrm{kg}^{2}$. The potential energy of the system is $-7.79 \times 10^{28} \mathrm{~J}$. The mean distance between the earth and moon is
138479 The gravitational field in a region is given by $\mathrm{g}=5 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{kg} \hat{\mathrm{i}}+12 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{kg} \hat{\mathbf{j}}$. The change in the gravitational potential energy of a particle of mass $1 \mathrm{~kg}$ when it is taken from the origin to a point $(7 m,-3 m)$ is:
138478 The mass of the earth is $6.00 \times 10^{24} \mathrm{~kg}$ and that of the moon is $7.40 \times 10^{22} \mathrm{~kg}$. The constant of gravitation $G=6.67 \times 10^{-1 i} \mathrm{~N}-\mathrm{m}^{2} / \mathrm{kg}^{2}$. The potential energy of the system is $-7.79 \times 10^{28} \mathrm{~J}$. The mean distance between the earth and moon is
138479 The gravitational field in a region is given by $\mathrm{g}=5 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{kg} \hat{\mathrm{i}}+12 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{kg} \hat{\mathbf{j}}$. The change in the gravitational potential energy of a particle of mass $1 \mathrm{~kg}$ when it is taken from the origin to a point $(7 m,-3 m)$ is: