371603
A cylinder of cross-section area \({A}\) has two pistons of negligible mass separated by distances \({l}\) loaded with spring of negligible mass. An ideal gas at temperature \({T_{1}}\) is in the cylinder where the springs are relaxed. When the gas is heated by some means its temperature becomes \({T_{2}}\) and the springs get compressed by \({\dfrac{l}{2}}\) each. If \({P_{0}}\) is atmospheric pressure and spring constant \({k=\dfrac{2 P_{0} A}{l}}\), then the ratio of \({T_{2}}\) and \({T_{1}}\) is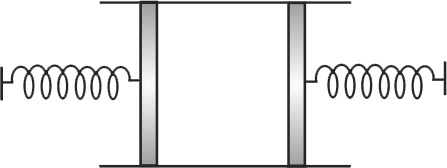
371607
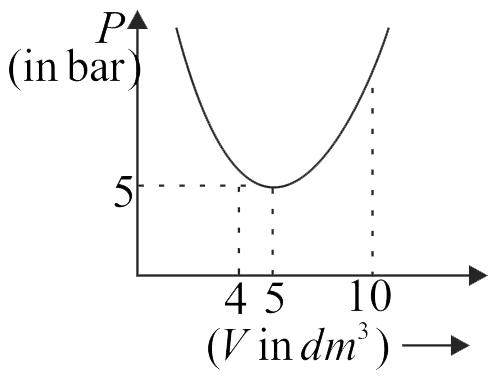
An ideal gas undergoes a process such that pressure is a parabolic function of volume with the function having its minima at \(P = 5\,bar,V = 5\,\,d{m^3}.\) If the volume is increased from \(4\,\,d{m^3}\) to \(10\,\,d{m^3},\) the work done in the process is
(\(1\) bar \({ = {{10}^5}\;Pa}\))
371603
A cylinder of cross-section area \({A}\) has two pistons of negligible mass separated by distances \({l}\) loaded with spring of negligible mass. An ideal gas at temperature \({T_{1}}\) is in the cylinder where the springs are relaxed. When the gas is heated by some means its temperature becomes \({T_{2}}\) and the springs get compressed by \({\dfrac{l}{2}}\) each. If \({P_{0}}\) is atmospheric pressure and spring constant \({k=\dfrac{2 P_{0} A}{l}}\), then the ratio of \({T_{2}}\) and \({T_{1}}\) is
371607
An ideal gas undergoes a process such that pressure is a parabolic function of volume with the function having its minima at \(P = 5\,bar,V = 5\,\,d{m^3}.\) If the volume is increased from \(4\,\,d{m^3}\) to \(10\,\,d{m^3},\) the work done in the process is
(\(1\) bar \({ = {{10}^5}\;Pa}\))
371603
A cylinder of cross-section area \({A}\) has two pistons of negligible mass separated by distances \({l}\) loaded with spring of negligible mass. An ideal gas at temperature \({T_{1}}\) is in the cylinder where the springs are relaxed. When the gas is heated by some means its temperature becomes \({T_{2}}\) and the springs get compressed by \({\dfrac{l}{2}}\) each. If \({P_{0}}\) is atmospheric pressure and spring constant \({k=\dfrac{2 P_{0} A}{l}}\), then the ratio of \({T_{2}}\) and \({T_{1}}\) is
371607
An ideal gas undergoes a process such that pressure is a parabolic function of volume with the function having its minima at \(P = 5\,bar,V = 5\,\,d{m^3}.\) If the volume is increased from \(4\,\,d{m^3}\) to \(10\,\,d{m^3},\) the work done in the process is
(\(1\) bar \({ = {{10}^5}\;Pa}\))
371603
A cylinder of cross-section area \({A}\) has two pistons of negligible mass separated by distances \({l}\) loaded with spring of negligible mass. An ideal gas at temperature \({T_{1}}\) is in the cylinder where the springs are relaxed. When the gas is heated by some means its temperature becomes \({T_{2}}\) and the springs get compressed by \({\dfrac{l}{2}}\) each. If \({P_{0}}\) is atmospheric pressure and spring constant \({k=\dfrac{2 P_{0} A}{l}}\), then the ratio of \({T_{2}}\) and \({T_{1}}\) is
371607
An ideal gas undergoes a process such that pressure is a parabolic function of volume with the function having its minima at \(P = 5\,bar,V = 5\,\,d{m^3}.\) If the volume is increased from \(4\,\,d{m^3}\) to \(10\,\,d{m^3},\) the work done in the process is
(\(1\) bar \({ = {{10}^5}\;Pa}\))