367867 Two polaroids are placed in the path of unpolarised beam of intensity \({I_0}\) such that no light is emitted from the second polaroid. If a third polaroid whose polarisation axis makes an angle \(\theta \) with the polarisation axis of first polaroid, is placed between these polaroids then the intensity of light emerging from the last polaroid will be
367868
Three polaroid sheets are co-axially placed as indicated in the diagram. Pass axes of the polaroids 2 and 3 make \({30^{\circ}}\) and \({90^{\circ}}\) with pass axis of polaroid sheet 1 . If \({I_{0}}\) is the intensity of the incident unpolarised light entering sheet 1 , the intensity of the emergent light through sheet 3 is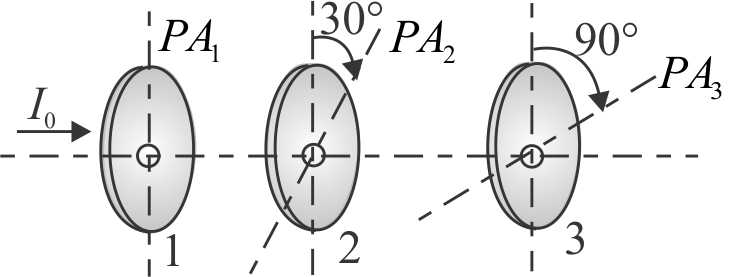
367869
A plane polarized beam of intensity \(I\) is incident on a polariser with the electric vector inclined at \(30^{\circ}\) to the optic axis of the polariser passes through an analyzer whose optic axis is inclined at \(30^{\circ}\) to that of polariser. Intensity of light coming out of the analyser is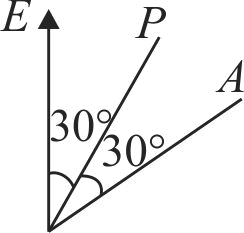
367870 A beam of natural light falls on a system of 5 polaroids, which are arranged in succession such that the pass axis of each polaroid is turned through \(60^\circ \) with respect to the preceding one. The fraction of the incident light intensity that passes through the system is
367867 Two polaroids are placed in the path of unpolarised beam of intensity \({I_0}\) such that no light is emitted from the second polaroid. If a third polaroid whose polarisation axis makes an angle \(\theta \) with the polarisation axis of first polaroid, is placed between these polaroids then the intensity of light emerging from the last polaroid will be
367868
Three polaroid sheets are co-axially placed as indicated in the diagram. Pass axes of the polaroids 2 and 3 make \({30^{\circ}}\) and \({90^{\circ}}\) with pass axis of polaroid sheet 1 . If \({I_{0}}\) is the intensity of the incident unpolarised light entering sheet 1 , the intensity of the emergent light through sheet 3 is
367869
A plane polarized beam of intensity \(I\) is incident on a polariser with the electric vector inclined at \(30^{\circ}\) to the optic axis of the polariser passes through an analyzer whose optic axis is inclined at \(30^{\circ}\) to that of polariser. Intensity of light coming out of the analyser is
367870 A beam of natural light falls on a system of 5 polaroids, which are arranged in succession such that the pass axis of each polaroid is turned through \(60^\circ \) with respect to the preceding one. The fraction of the incident light intensity that passes through the system is
367867 Two polaroids are placed in the path of unpolarised beam of intensity \({I_0}\) such that no light is emitted from the second polaroid. If a third polaroid whose polarisation axis makes an angle \(\theta \) with the polarisation axis of first polaroid, is placed between these polaroids then the intensity of light emerging from the last polaroid will be
367868
Three polaroid sheets are co-axially placed as indicated in the diagram. Pass axes of the polaroids 2 and 3 make \({30^{\circ}}\) and \({90^{\circ}}\) with pass axis of polaroid sheet 1 . If \({I_{0}}\) is the intensity of the incident unpolarised light entering sheet 1 , the intensity of the emergent light through sheet 3 is
367869
A plane polarized beam of intensity \(I\) is incident on a polariser with the electric vector inclined at \(30^{\circ}\) to the optic axis of the polariser passes through an analyzer whose optic axis is inclined at \(30^{\circ}\) to that of polariser. Intensity of light coming out of the analyser is
367870 A beam of natural light falls on a system of 5 polaroids, which are arranged in succession such that the pass axis of each polaroid is turned through \(60^\circ \) with respect to the preceding one. The fraction of the incident light intensity that passes through the system is
367867 Two polaroids are placed in the path of unpolarised beam of intensity \({I_0}\) such that no light is emitted from the second polaroid. If a third polaroid whose polarisation axis makes an angle \(\theta \) with the polarisation axis of first polaroid, is placed between these polaroids then the intensity of light emerging from the last polaroid will be
367868
Three polaroid sheets are co-axially placed as indicated in the diagram. Pass axes of the polaroids 2 and 3 make \({30^{\circ}}\) and \({90^{\circ}}\) with pass axis of polaroid sheet 1 . If \({I_{0}}\) is the intensity of the incident unpolarised light entering sheet 1 , the intensity of the emergent light through sheet 3 is
367869
A plane polarized beam of intensity \(I\) is incident on a polariser with the electric vector inclined at \(30^{\circ}\) to the optic axis of the polariser passes through an analyzer whose optic axis is inclined at \(30^{\circ}\) to that of polariser. Intensity of light coming out of the analyser is
367870 A beam of natural light falls on a system of 5 polaroids, which are arranged in succession such that the pass axis of each polaroid is turned through \(60^\circ \) with respect to the preceding one. The fraction of the incident light intensity that passes through the system is
