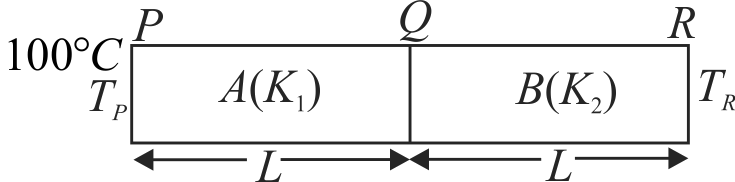
366420 Two slabs \(A\) and \(B\) of different materials but of the same thickness are joined end to end to form a composite slab. The thermal conductivities of A and B are \(K_{1}\) and \(K_{2}\), respectively. A steady temperature difference of \(12^\circ C\) is maintained across the composite slab. If \(K_{1}=\dfrac{K_{2}}{2}\), the temperature difference across slab \(A\) is
366422 A partition Wall has two layers \(A\) and \(B\), in contact, each made of a different material. They have the same thickness but the thermal conductivity of layer \(A\) is twice that of layer \(B\). If the steady state temperature difference across the wall is \(60\;K\), then the corresponding difference across the layer \(A\) is
366420 Two slabs \(A\) and \(B\) of different materials but of the same thickness are joined end to end to form a composite slab. The thermal conductivities of A and B are \(K_{1}\) and \(K_{2}\), respectively. A steady temperature difference of \(12^\circ C\) is maintained across the composite slab. If \(K_{1}=\dfrac{K_{2}}{2}\), the temperature difference across slab \(A\) is
366422 A partition Wall has two layers \(A\) and \(B\), in contact, each made of a different material. They have the same thickness but the thermal conductivity of layer \(A\) is twice that of layer \(B\). If the steady state temperature difference across the wall is \(60\;K\), then the corresponding difference across the layer \(A\) is
366420 Two slabs \(A\) and \(B\) of different materials but of the same thickness are joined end to end to form a composite slab. The thermal conductivities of A and B are \(K_{1}\) and \(K_{2}\), respectively. A steady temperature difference of \(12^\circ C\) is maintained across the composite slab. If \(K_{1}=\dfrac{K_{2}}{2}\), the temperature difference across slab \(A\) is
366422 A partition Wall has two layers \(A\) and \(B\), in contact, each made of a different material. They have the same thickness but the thermal conductivity of layer \(A\) is twice that of layer \(B\). If the steady state temperature difference across the wall is \(60\;K\), then the corresponding difference across the layer \(A\) is
366420 Two slabs \(A\) and \(B\) of different materials but of the same thickness are joined end to end to form a composite slab. The thermal conductivities of A and B are \(K_{1}\) and \(K_{2}\), respectively. A steady temperature difference of \(12^\circ C\) is maintained across the composite slab. If \(K_{1}=\dfrac{K_{2}}{2}\), the temperature difference across slab \(A\) is
366422 A partition Wall has two layers \(A\) and \(B\), in contact, each made of a different material. They have the same thickness but the thermal conductivity of layer \(A\) is twice that of layer \(B\). If the steady state temperature difference across the wall is \(60\;K\), then the corresponding difference across the layer \(A\) is