361184
A cube of side \(a\) and mass \(m\) just floats on the surface of water as shown in the figure. The surface tension and density of water are \(T\) and \(\rho\), respectively. If angle of contact between cube and water surface is zero, find the distance \(h\) (in metres) between the lower face of cube and surface of the water.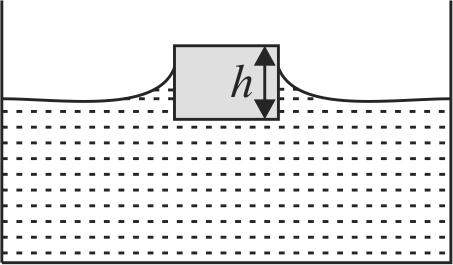
361184
A cube of side \(a\) and mass \(m\) just floats on the surface of water as shown in the figure. The surface tension and density of water are \(T\) and \(\rho\), respectively. If angle of contact between cube and water surface is zero, find the distance \(h\) (in metres) between the lower face of cube and surface of the water.
361184
A cube of side \(a\) and mass \(m\) just floats on the surface of water as shown in the figure. The surface tension and density of water are \(T\) and \(\rho\), respectively. If angle of contact between cube and water surface is zero, find the distance \(h\) (in metres) between the lower face of cube and surface of the water.
361184
A cube of side \(a\) and mass \(m\) just floats on the surface of water as shown in the figure. The surface tension and density of water are \(T\) and \(\rho\), respectively. If angle of contact between cube and water surface is zero, find the distance \(h\) (in metres) between the lower face of cube and surface of the water.
361184
A cube of side \(a\) and mass \(m\) just floats on the surface of water as shown in the figure. The surface tension and density of water are \(T\) and \(\rho\), respectively. If angle of contact between cube and water surface is zero, find the distance \(h\) (in metres) between the lower face of cube and surface of the water.