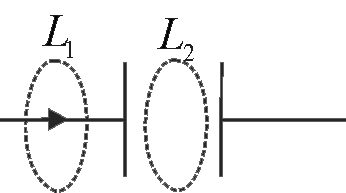
358766 A parallel plate capacitor consists of two circular plates of radius \(0.1\;m\). They are separated by a distance \(0.5\;mm\). If electric field between the capacitor plates changes as \(\frac{{dE}}{{dt}} = 5 \times {10^{13}}\frac{V}{{m \times s}}\) find displacement current between the plates.
358766 A parallel plate capacitor consists of two circular plates of radius \(0.1\;m\). They are separated by a distance \(0.5\;mm\). If electric field between the capacitor plates changes as \(\frac{{dE}}{{dt}} = 5 \times {10^{13}}\frac{V}{{m \times s}}\) find displacement current between the plates.
358766 A parallel plate capacitor consists of two circular plates of radius \(0.1\;m\). They are separated by a distance \(0.5\;mm\). If electric field between the capacitor plates changes as \(\frac{{dE}}{{dt}} = 5 \times {10^{13}}\frac{V}{{m \times s}}\) find displacement current between the plates.
358766 A parallel plate capacitor consists of two circular plates of radius \(0.1\;m\). They are separated by a distance \(0.5\;mm\). If electric field between the capacitor plates changes as \(\frac{{dE}}{{dt}} = 5 \times {10^{13}}\frac{V}{{m \times s}}\) find displacement current between the plates.