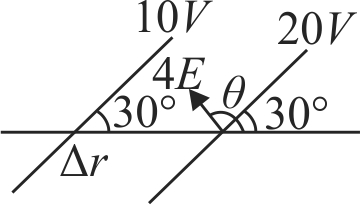
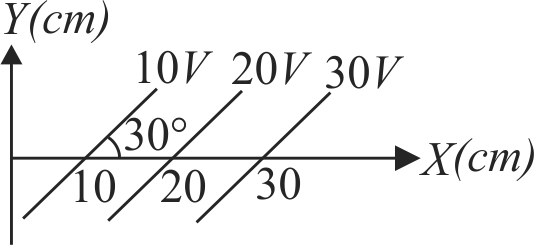359534 Assume that an electric field \(\overrightarrow E = 30{{\rm{x}}^2}\hat i\) exists in space. Then the potential difference \({V_A} - {V_O}\), where \({V_O}\) is the potential at the origin and \({V_A}\) the potential at \({\rm{x = }}2{\rm{m}}\) is
359534 Assume that an electric field \(\overrightarrow E = 30{{\rm{x}}^2}\hat i\) exists in space. Then the potential difference \({V_A} - {V_O}\), where \({V_O}\) is the potential at the origin and \({V_A}\) the potential at \({\rm{x = }}2{\rm{m}}\) is
359534 Assume that an electric field \(\overrightarrow E = 30{{\rm{x}}^2}\hat i\) exists in space. Then the potential difference \({V_A} - {V_O}\), where \({V_O}\) is the potential at the origin and \({V_A}\) the potential at \({\rm{x = }}2{\rm{m}}\) is
359534 Assume that an electric field \(\overrightarrow E = 30{{\rm{x}}^2}\hat i\) exists in space. Then the potential difference \({V_A} - {V_O}\), where \({V_O}\) is the potential at the origin and \({V_A}\) the potential at \({\rm{x = }}2{\rm{m}}\) is