359388
The figure given below shows four arrangement of charged particles, all at the same distance from the origin. Rank the situations according to the net electric potential \({\left(V_{1}, V_{2}, V_{3}, V_{4}\right)}\) at the origin, most positive first.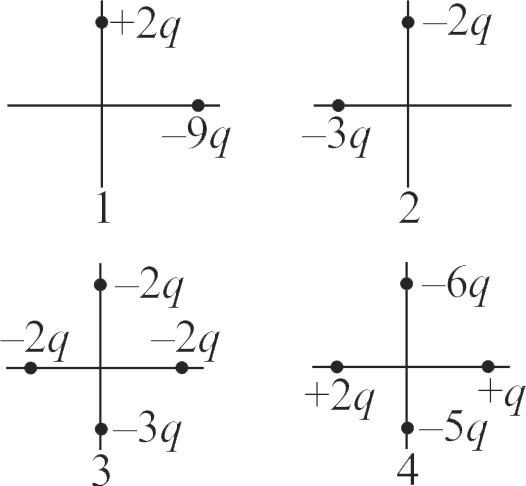
359391
Assertion :
On going away from a point charge or a small electric dipole, electric potential decreases at the same rate in both the cases.
Reason :
Electric potential is inversely proportional to square of distance from the charge in case of dipole.
359388
The figure given below shows four arrangement of charged particles, all at the same distance from the origin. Rank the situations according to the net electric potential \({\left(V_{1}, V_{2}, V_{3}, V_{4}\right)}\) at the origin, most positive first.
359391
Assertion :
On going away from a point charge or a small electric dipole, electric potential decreases at the same rate in both the cases.
Reason :
Electric potential is inversely proportional to square of distance from the charge in case of dipole.
359388
The figure given below shows four arrangement of charged particles, all at the same distance from the origin. Rank the situations according to the net electric potential \({\left(V_{1}, V_{2}, V_{3}, V_{4}\right)}\) at the origin, most positive first.
359391
Assertion :
On going away from a point charge or a small electric dipole, electric potential decreases at the same rate in both the cases.
Reason :
Electric potential is inversely proportional to square of distance from the charge in case of dipole.
359388
The figure given below shows four arrangement of charged particles, all at the same distance from the origin. Rank the situations according to the net electric potential \({\left(V_{1}, V_{2}, V_{3}, V_{4}\right)}\) at the origin, most positive first.
359391
Assertion :
On going away from a point charge or a small electric dipole, electric potential decreases at the same rate in both the cases.
Reason :
Electric potential is inversely proportional to square of distance from the charge in case of dipole.