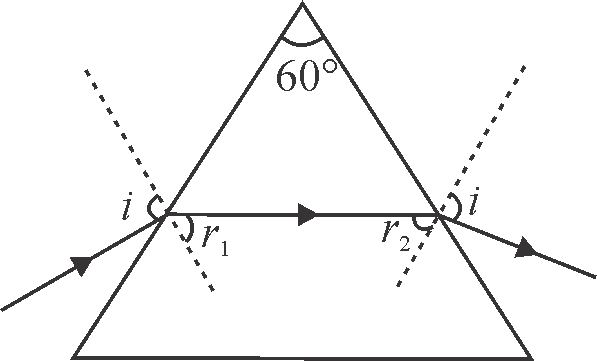
365093 A prism of certain angle deviates the red and blue rays by \(8^\circ \) and \(12^\circ \) respectively. Another prism of the same angle deviates the red and blue rays by \(10^\circ \) and \(14^\circ \) respectively. The prisms are small angled and made of different materials. The dispersive powers of the materials of the prisms are in the ratio
365094 A thin prism \(P_{1}\) of angle \(4^{\circ}\), are made from a glass of refractive index 1.54, is combined with another thin prism \(P_{2}\) made from a glass of refractive index 1.72 , to produce dispersion without deviation. The angle of \(P_{2}\) is:
365095
A parallel glass slab of refractive index \({\sqrt{3}}\) is placed in contact with an equilateral prism of refractive index \({\sqrt{2}}\). A ray is incident on left surface of slab as shown. The slab and prism combination is surrounded by air. Find the magnitude of minimum possible deviation of this ray by slab-prism combination.
365093 A prism of certain angle deviates the red and blue rays by \(8^\circ \) and \(12^\circ \) respectively. Another prism of the same angle deviates the red and blue rays by \(10^\circ \) and \(14^\circ \) respectively. The prisms are small angled and made of different materials. The dispersive powers of the materials of the prisms are in the ratio
365094 A thin prism \(P_{1}\) of angle \(4^{\circ}\), are made from a glass of refractive index 1.54, is combined with another thin prism \(P_{2}\) made from a glass of refractive index 1.72 , to produce dispersion without deviation. The angle of \(P_{2}\) is:
365095
A parallel glass slab of refractive index \({\sqrt{3}}\) is placed in contact with an equilateral prism of refractive index \({\sqrt{2}}\). A ray is incident on left surface of slab as shown. The slab and prism combination is surrounded by air. Find the magnitude of minimum possible deviation of this ray by slab-prism combination.
365093 A prism of certain angle deviates the red and blue rays by \(8^\circ \) and \(12^\circ \) respectively. Another prism of the same angle deviates the red and blue rays by \(10^\circ \) and \(14^\circ \) respectively. The prisms are small angled and made of different materials. The dispersive powers of the materials of the prisms are in the ratio
365094 A thin prism \(P_{1}\) of angle \(4^{\circ}\), are made from a glass of refractive index 1.54, is combined with another thin prism \(P_{2}\) made from a glass of refractive index 1.72 , to produce dispersion without deviation. The angle of \(P_{2}\) is:
365095
A parallel glass slab of refractive index \({\sqrt{3}}\) is placed in contact with an equilateral prism of refractive index \({\sqrt{2}}\). A ray is incident on left surface of slab as shown. The slab and prism combination is surrounded by air. Find the magnitude of minimum possible deviation of this ray by slab-prism combination.
365093 A prism of certain angle deviates the red and blue rays by \(8^\circ \) and \(12^\circ \) respectively. Another prism of the same angle deviates the red and blue rays by \(10^\circ \) and \(14^\circ \) respectively. The prisms are small angled and made of different materials. The dispersive powers of the materials of the prisms are in the ratio
365094 A thin prism \(P_{1}\) of angle \(4^{\circ}\), are made from a glass of refractive index 1.54, is combined with another thin prism \(P_{2}\) made from a glass of refractive index 1.72 , to produce dispersion without deviation. The angle of \(P_{2}\) is:
365095
A parallel glass slab of refractive index \({\sqrt{3}}\) is placed in contact with an equilateral prism of refractive index \({\sqrt{2}}\). A ray is incident on left surface of slab as shown. The slab and prism combination is surrounded by air. Find the magnitude of minimum possible deviation of this ray by slab-prism combination.